Have you ever peered into the heart of your computer, curious about the intricate network of components that bring your digital world to life? The motherboard, often referred to as the “backbone” of a computer, is where it all starts. This complex board houses the central processing unit (CPU), memory modules, expansion slots, and countless other essential components, all interconnected in a carefully orchestrated dance.
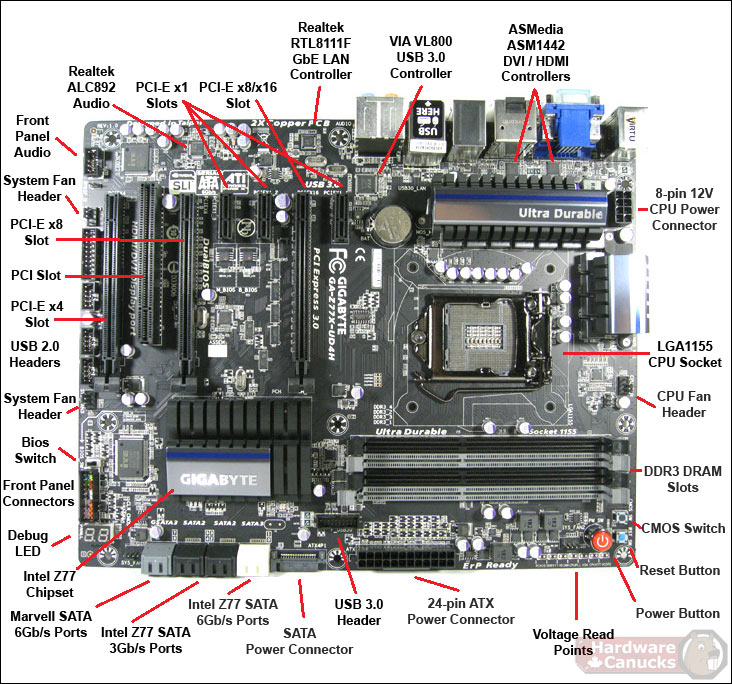
Image: wirediagramrefugio.z21.web.core.windows.net
Understanding the layout and functions of a motherboard can be crucial, whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or a curious beginner. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the anatomy of a motherboard, providing a detailed diagram with clear labels explaining each element and its role. By the end, you’ll have a clear grasp of the motherboard’s functionality and its vital role in a computer’s operation.
Unlocking the Mysteries of the Motherboard
The motherboard, at its core, is a printed circuit board (PCB) that serves as the foundation for all other computer components. It provides the physical connections and pathways for data to flow seamlessly between the CPU, memory, storage drives, and peripherals.
Imagine a bustling city where each building represents a different component. The motherboard acts as the city’s infrastructure, connecting all the buildings with roads, power lines, and communication channels. Without the motherboard, there would be no way for these components to interact efficiently, leading to a dysfunctional system.
A Closer Look at the Motherboard’s Anatomy
1. The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU, often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, sits at the heart of the motherboard. It’s responsible for executing instructions, processing data, and managing the flow of information throughout the system. This is where the “real work” gets done, from running your favorite games to editing photos and browsing the web.
![[DIAGRAM] Asus Motherboard Diagram With Labels - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://images.anandtech.com/doci/6964/Gigabyte Z77-HD4 - Schematic.jpg)
Image: mydiagram.online
2. Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM, also known as “short-term memory,” is used to temporarily store data and programs currently being used by the CPU. Think of it as the computer’s scratchpad where it quickly accesses things it needs at a particular moment. The more RAM you have, the faster and smoother your computer will operate, especially when multitasking or running demanding applications.
3. Chipset
The chipset acts as the central controller for communication between the CPU, RAM, and other peripherals. It’s essentially a set of microchips that handle the flow of data between different components on the motherboard.
4. Expansion Slots
Expansion slots allow you to add extra components like graphics cards, sound cards, and other peripherals. These slots vary in type, with different sizes and connectors designed for specific functionalities.
5. BIOS Chip
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a small chip that contains instructions for the computer to boot up. It’s responsible for initializing the system’s hardware and loading the operating system when you turn on your computer.
6. Power Supply Connectors
The motherboard includes connectors for the power supply unit (PSU), which provides electrical power to all components. These connectors come in various sizes and configurations, depending on the type of PSU used.
7. Storage Device Connectors
These connectors are used to attach storage devices like hard drives and solid state drives (SSDs). They allow the motherboard to access and store data on these drives.
8. Input/Output (I/O) Ports
I/O ports are used to connect external devices, such as keyboards, mice, monitors, printers, and USB drives. These ports vary in type and number depending on the motherboard’s design.
Staying Up-to-Date with Motherboard Trends
The world of computer technology is constantly evolving, and motherboards are no exception. New advancements in CPU technology, memory standards, and connectivity options are rolled out regularly.
To stay abreast of the latest trends, it’s recommended to keep an eye on industry publications, tech forums, and reputable online retailers. Forums like Reddit’s r/buildapc provide a wealth of information and advice from experienced enthusiasts. Staying informed about the latest technologies will help you make informed decisions when choosing and upgrading your motherboard.
Expert Advice for Navigating the Motherboard Maze
Choosing the right motherboard can be daunting, considering the plethora of options available. Here are some expert tips to guide you:
1. **Determine your needs:** Before venturing into the motherboard market, assess your requirements. Is it for a gaming rig, a workstation, or a general-purpose PC? Your specific needs will help narrow down the choices.
2. **Match your CPU and RAM:** Ensure your chosen motherboard is compatible with your CPU and RAM. You’ll need to check the motherboard’s specifications and ensure it supports the desired CPU socket type and RAM modules.
3. **Consider future upgradeability:** Look for a motherboard with plenty of expansion slots and connector options to allow for future upgrades. This will give you room to grow and enhance your system’s performance in the years to come.
4. **Don’t overlook the chipset:** The chipset plays a crucial role in determining the motherboard’s overall capabilities. Opt for a chipset that balances features and performance according to your specific requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions About Motherboards
Q: What is the difference between an ATX and a Micro-ATX motherboard?
A: ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) is a standard motherboard form factor with dimensions of 12 inches x 9.6 inches. Micro-ATX (μATX) is a smaller version, typically measuring 9.6 inches x 9.6 inches, with fewer expansion slots and ports.
Q: What is the difference between a CPU socket and a RAM slot?
A: The CPU socket is the physical connection point on the motherboard where the CPU is installed. RAM slots hold the memory modules, which are responsible for temporarily storing data used by the CPU.
Q: How do I choose the right power supply for my motherboard?
A: The power supply needs to provide enough wattage to power all the components in your system. Consult your motherboard’s specifications to determine the recommended power supply wattage. Also, consider the power consumption of your CPU, GPU, and other components.
Q: Are all motherboards compatible with all graphics cards?
A: Not all motherboards are compatible with all graphics cards. You need to ensure that the motherboard’s expansion slots (typically PCIe slots) are compatible with the graphics card you’re planning to use. The motherboard’s specifications will outline the compatible graphics card types.
Q: Can I upgrade my motherboard without replacing other components?
A: It’s possible, but not always advisable. Changing your motherboard can lead to incompatibility issues with existing components, such as the CPU, RAM, and storage drives. It’s essential to check the compatibility of your current components with the new motherboard before making any changes.
Diagram Of A Motherboard With Labels
Concluding Thoughts: A Journey into the Motherboard’s Heart
As you’ve journeyed through this article, you’ve gained a deeper understanding of the motherboard’s crucial role in a computer’s operation. These intricate boards, with their intricate network of components, seamlessly connect the digital world to your fingertips.
Remember, choosing the right motherboard can be a significant decision, impacting your system’s performance and potential for future upgrades. Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, you’re ready to confidently navigate the motherboard landscape and choose the one that best fits your needs.
Are you interested in learning more about specific motherboard models or specific components like the CPU and RAM? Let us know in the comments below, and we’ll delve deeper into these fascinating aspects of computer hardware.






