Have you ever wondered how scientists come up with their conclusions? The answer lies in the careful design of experiments, where variables play a crucial role. Understanding the difference between independent, dependent, and controlled variables is essential for conducting meaningful research. In this article, we’ll explore these concepts in detail, providing clear explanations and a downloadable worksheet with answers to help you solidify your grasp on this fundamental scientific principle.

Image: classpropst.z19.web.core.windows.net
Let’s imagine you’re trying to figure out if adding fertilizer makes plants grow taller. This simple experiment involves several key components, each representing a different type of variable. The amount of fertilizer you add is the independent variable, which you control. The height of the plants is the dependent variable, as it changes in response to the independent variable. Finally, you need to keep certain factors constant, like the type of plant, the amount of sunlight, and the watering schedule – these are the controlled variables.
Understanding Variables in Scientific Experiments
Independent Variable: The Cause
The independent variable is the factor that you change or manipulate in an experiment. It’s the “cause” that you’re investigating to see if it has any effect. Think of it as the input you’re giving the system. In our plant growth example, the amount of fertilizer is the independent variable. We’re changing the amount of fertilizer to observe its effect on plant height.
Dependent Variable: The Effect
The dependent variable is the factor that is measured or observed in an experiment. It’s the “effect” that you’re trying to determine. This variable is dependent on the independent variable; it’s the output of the system. In our example, the plant’s height is the dependent variable. Its height depends on how much fertilizer we apply.
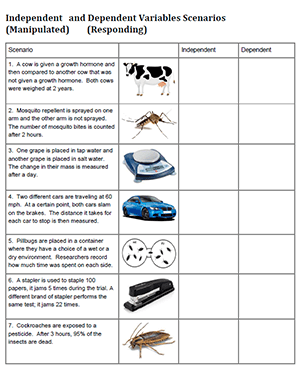
Image: martindxmguide.blogspot.com
Controlled Variables: Keeping Things Constant
Controlled variables are the factors that you keep the same throughout the experiment. They help ensure that any changes in the dependent variable are truly due to the independent variable and not some other factor. Think of them as background conditions that need to be consistent for a valid experiment. In our plant growth example, controlled variables would include the type of plant, the amount of sunlight, and the watering schedule. If we change any of these factors, it might influence the plant’s height, making it difficult to pinpoint the effect of fertilizer alone.
The Power of Controlled Experiments
By carefully controlling variables, scientists can isolate the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. This allows them to draw conclusions about cause and effect. For example, in our plant growth experiment, if we see that plants grow taller with more fertilizer, we can reasonably conclude that fertilizer has a positive effect on plant height.
However, if we don’t control for other factors, like the amount of sunlight or water, it becomes difficult to determine whether the increase in plant height is due to fertilizer or these other variables. Controlled experiments help ensure a more accurate and reliable determination of cause and effect.
Real-World Applications of Variables
The concept of variables isn’t just for scientists in labs – it applies to everyday life as well. Imagine you’re trying to bake a cake. The independent variable might be the amount of sugar you add. The dependent variable is the cake’s sweetness. Controlled variables include the type of flour, the baking time, and the oven temperature. Understanding these variables can help you create the perfect cake every time.
Tips for Identifying Variables
Identifying variables in an experiment can be tricky at first, but here are some tips:
- Think about the question you’re trying to answer: This will help you determine the cause (independent variable) and the effect (dependent variable).
- Consider what factors you’re manipulating: This will identify the independent variable.
- Ask yourself what you’re measuring: This will reveal the dependent variable.
- Identify any factors that need to be kept constant: These are your controlled variables.
By following these tips, you can clearly define the variables in your experiments and ensure that your results are meaningful and reliable.
Independent, Dependent, and Controlled Variables Worksheet with Answers PDF
To further enhance your understanding of variables, we’ve created a downloadable worksheet with answers: Independent, Dependent, and Controlled Variables Worksheet. This worksheet provides various scenarios and prompts you to identify the independent, dependent, and controlled variables in each case. The answers are included to help you check your work and solidify your understanding.
FAQs About Variables
What is the difference between a variable and a constant?
A variable is a factor that can change or vary in an experiment, while a constant remains the same. Controlled variables are constants, and the independent variable is the one that you intentionally change.
Can there be more than one independent variable in an experiment?
Yes, an experiment can have multiple independent variables. However, it’s important to design the experiment in a way that allows you to isolate the effect of each independent variable on the dependent variable.
What are some common mistakes people make when identifying variables?
A common mistake is confusing the independent and dependent variables. Remember that the independent variable is the one you manipulate, and the dependent variable is the one you measure. Another mistake is neglecting to identify controlled variables, which can lead to inaccurate results.
Independent Dependent And Controlled Variables Worksheet With Answers Pdf
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between independent, dependent, and controlled variables is crucial for conducting meaningful scientific experiments. By carefully identifying and controlling variables, you can ensure that your results are reliable and that you can draw accurate conclusions about cause and effect. We hope this article has provided you with a clear understanding of these concepts. You can enhance your knowledge further by downloading the provided worksheet with answers. Good luck on your scientific endeavors! Are you interested in learning more about designing scientific experiments or have any questions about variables? Let us know in the comments below.






