Have you ever found yourself struggling to choose the right form of a verb? Do the words “present,” “past,” and “past participle” leave you feeling confused? You’re not alone! These verb forms are fundamental to constructing grammatically correct sentences, and understanding them can unlock a whole new level of confidence in your writing and speaking.
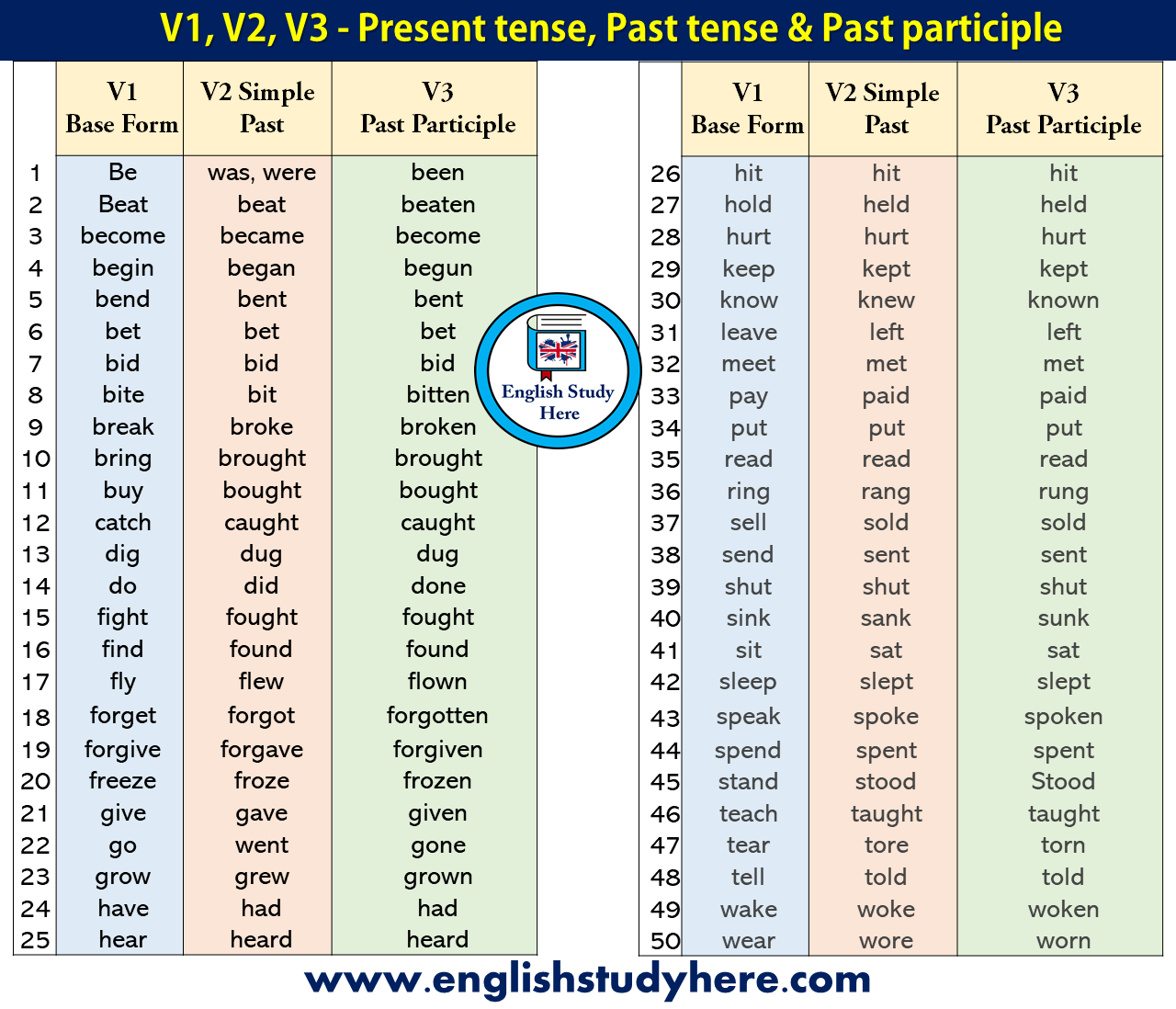
Image: lopersyoga.weebly.com
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll embark on a journey through the world of verbs, exploring the nuances of present, past, and past participle forms. We’ll delve into their definitions, explore their usage in various contexts, and equip you with the knowledge to confidently employ them in your own language. So, buckle up, because we’re about to unravel the secrets of verb conjugation!
Defining the Trio: Present, Past, and Past Participle
Before we dive into the depths of verb forms, let’s establish a clear understanding of what each one represents.
Present Tense: Capturing the Now
The present tense is the simplest and most straightforward form of a verb. It describes actions that are happening right now, as we speak. Think of it as a snapshot of the action in the moment!
Examples:
- I walk to school every morning.
- The birds sing merrily in the trees.
Past Tense: Reflecting on the Past
The past tense takes us back in time, reflecting on actions that have already happened. It tells us what occurred in the past, whether it was yesterday, last week, or many years ago.
Examples:
- I walked to school yesterday.
- The birds sang beautifully in the garden last night.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Past Participle: A Multifaceted Form
The past participle is a bit more versatile than its siblings. It acts as both a verb form and an adjective, offering a broad range of applications. Let’s break it down:
The Past Participle as a Verb
In this role, the past participle often joins forces with auxiliary verbs, such as “have,” “has,” or “had,” to create compound verb tenses, including the present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect.
Examples:
- I have walked 10 miles today.
- The birds had sung a beautiful song before the storm arrived.
The Past Participle as an Adjective
The past participle also has a knack for describing nouns, acting as a descriptive adjective. This is especially common in past perfect and present perfect sentences.
Examples:
- I am exhausted after that long hike.
- The baked cookies filled the house with a delightful aroma.
The Irregular Verbs: A Special Case
While most verbs follow a predictable pattern of adding “-ed” to form the past tense and past participle, some verbs deviate from the norm. These are known as irregular verbs, and they often present a challenge for learners.
Examples of irregular verbs:
- Go, went, gone
- See, saw, seen
- Do, did, done
The best way to master irregular verbs is to memorize them, just like learning a new vocabulary word. However, don’t fret! With regular practice and the use of helpful resources, such as flashcards or verb conjugation tables, you’ll be able to confidently navigate the world of irregular verbs.
The Present Perfect: A Bridge Between Past and Present
The present perfect tense is formed by combining the auxiliary verb “have” or “has” with the past participle form of the main verb. This tense is unique in that it connects the past and present, highlighting an action that began in the past and continues to have an effect in the present.
Examples:
- I have lived in this city for ten years.
- She has studied French since she was a child.
The Past Perfect: Focusing on a Past Action Before Another Past Event
As the name suggests, the past perfect tense places emphasis on past actions, but with a twist! It describes an action that happened before another past action. This tense is crucial for establishing a timeline of events in the past.
Examples:
- I had eaten breakfast before I went to work.
- They had finished their homework by the time the teacher came in.
The Future Perfect: Looking Ahead to the Completion of an Action
The future perfect tense transports us to the future, focusing on an action that will be completed by a specific time or event. It expresses the state of being after a future event.
Examples:
- I will have finished my presentation by tomorrow.
- They will have visited all the museums by the end of the trip.
Using Verbs Correctly: A Key to Effective Communication
In the vast tapestry of language, verbs are the threads that weave together ideas, actions, and emotions. Mastering the present, past, and past participle forms of verbs is essential for clear, concise, and accurate communication.
Whether it’s writing an email, writing a blog post, or conversing with friends, a solid understanding of verb conjugation equips you to express yourself with precision and fluency.
Present Past Past Participle 100 Words
Continuing the Journey
This exploration of verbs is just the beginning. There’s a world of verb tenses, moods, and voices waiting to be unlocked. We encourage you to continue your grammatical journey, explore further resources, and practice, practice, practice!
With dedication and a thirst for knowledge, you can confidently navigate the often-confusing but compelling world of verbs. Remember, mastering verbs is an ongoing process, but every step you take strengthens your communication skills and expands your linguistic abilities.






