Imagine you’re enjoying a delicious meal, savoring each bite. But have you ever stopped to think about the intricate journey that food takes within your body? From the moment you swallow that first morsel, a complex symphony of processes begins, involving a remarkable organ system known as the digestive system. This system, orchestrated by the body’s metabolism, breaks down food into usable nutrients, absorbing them into the bloodstream and eliminating the waste products. It’s a fundamental process that sustains life, ensuring we have the energy and building blocks needed for growth, repair, and overall well-being.

Image: www.studypool.com
This chapter dives deep into the digestive system and its intimate connection with metabolism, exploring the fascinating mechanisms that govern how our bodies extract energy and nutrients from the food we consume. We’ll unravel the roles of different organs, the chemical reactions that fuel our cells, and the crucial dance between digestion and metabolism. Let’s embark on this journey to understand the underpinnings of our body’s remarkable ability to transform food into life.
The Digestive System: A Journey Through the Body
The digestive system is essentially a long, winding tube that extends from the mouth to the anus. This tube, known as the alimentary canal, is composed of several specialized organs, each contributing to the breakdown and absorption of food. The process begins in the mouth, where teeth and saliva work together to physically and chemically break down food. The food then travels through the esophagus, a muscular tube, into the stomach, where powerful acids and enzymes continue the digestive process.
Next, the partially digested food enters the small intestine, the primary site for nutrient absorption. Here, enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver work in concert to further break down food, allowing nutrients to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Finally, the remaining waste travels through the large intestine, where water is reabsorbed before being eliminated as feces. Throughout this journey, the digestive system is supported by accessory organs like the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, each playing a vital role in the overall process.
Metabolism: The Body’s Chemical Symphony
Metabolism encompasses all the chemical reactions that occur within our cells to sustain life. These reactions involve breaking down complex molecules (catabolism) to release energy and building up new molecules (anabolism) using that energy. The breakdown of food through the digestive system provides the necessary fuel for these metabolic processes.
Two key metabolic pathways are central to energy production: glycolysis and cellular respiration. Glycolysis, the initial stage of glucose breakdown, occurs in the cytoplasm of cells. This process converts glucose into pyruvate, releasing a small amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of cells. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondria, where the remaining stages of cellular respiration take place, involving the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. These processes efficiently generate ATP, providing the energy necessary for all cellular functions.
Understanding the Digestive System and Metabolic Connection
The digestive system and metabolism are intricately intertwined, each influencing and relying on the other for optimal functioning. Digestion is essential for providing the building blocks and energy sources needed for metabolism. Conversely, metabolism regulates the processes that digest food, controlling the release of enzymes and hormones involved in nutrient breakdown and absorption.
For example, hormones like insulin and glucagon play crucial roles in regulating blood sugar levels, which directly impacts metabolic processes. Insulin, released after a meal, promotes glucose uptake by cells, lowering blood sugar levels. Glucagon, secreted during periods of fasting, stimulates the release of stored glucose, raising blood sugar levels. These hormones act in concert to maintain a delicate balance in the body, ensuring that cells have a constant supply of energy.
Moreover, the digestive system plays a crucial role in absorbing essential vitamins and minerals, which are vital components of numerous metabolic reactions. For instance, vitamin B12 is essential for the formation of red blood cells and for proper nerve function. Iron is a key component of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. These nutrients, absorbed during digestion, are essential for maintaining a healthy metabolic state.
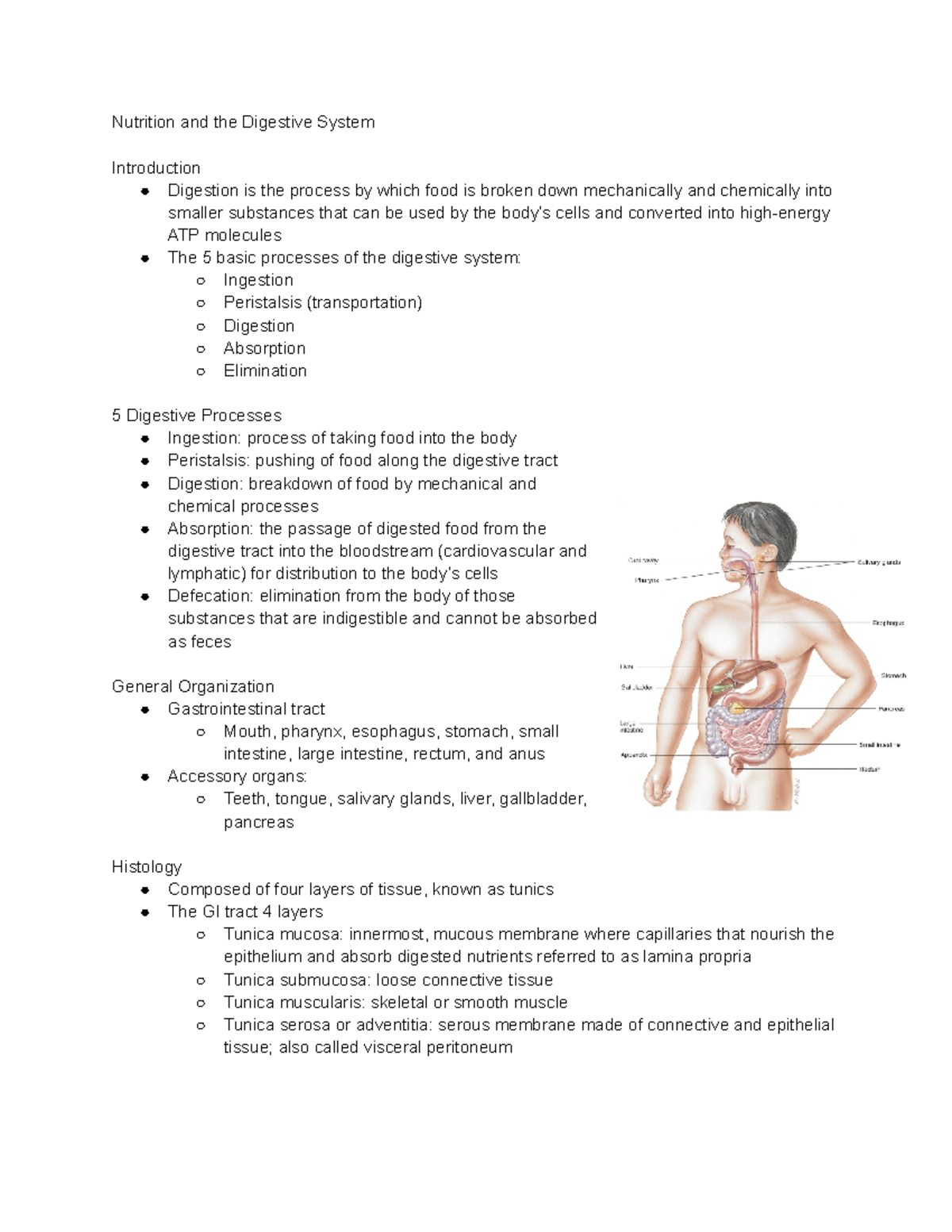
Image: www.studocu.com
Latest Trends and Developments
Research into the digestive system and metabolism is constantly evolving, shedding light on new insights and potential therapeutic avenues. For example, the microbiome, the community of microorganisms residing in our gut, is increasingly recognized for its profound impact on digestion and metabolism. Studies have linked specific gut bacteria to altered metabolic processes, affecting factors such as obesity, diabetes, and even brain function.
Emerging research suggests that personalized nutrition strategies, based on individual genetic profiles and gut microbiome composition, may hold promise for optimizing digestive health and metabolic well-being. This personalized approach could lead to more targeted dietary recommendations and lifestyle interventions tailored to individual needs, potentially improving overall health outcomes.
Expert Tips for Optimizing Digestive Health and Metabolism
Maintaining a healthy digestive system and optimal metabolic function is essential for overall well-being. Here are some practical tips grounded in current research and evidence-based practices:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Prioritize fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains.
- Stay Hydrated: Water is essential for proper digestion and absorption. Aim for 8-10 glasses of water daily.
- Manage Stress Levels: Chronic stress can disrupt digestion and metabolism. Engage in relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Consider Prebiotics and Probiotics: These supplements can support the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, promoting gut health and potentially influencing metabolism.
- Get Regular Exercise: Physical activity is crucial for boosting metabolism and maintaining a healthy weight, which can have positive impacts on digestive health.
These tips, combined with a mindful approach to eating and lifestyle choices, can significantly improve your digestive health and optimize your body’s metabolic processes. It’s important to remember that everyone is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the key organs involved in digestion?
The main organs involved in digestion are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Q: What are the main metabolic pathways?
The two main metabolic pathways involved in energy production are glycolysis and cellular respiration.
Q: How does stress affect digestion and metabolism?
Chronic stress can disrupt hormone balance, alter gut motility, and increase inflammation, negatively impacting digestion and metabolism.
Q: What are the benefits of a healthy gut microbiome?
A healthy gut microbiome is linked to improved digestion, a stronger immune system, better mental health, and a reduced risk of certain chronic diseases.
Q: Can I improve my digestion and metabolism through lifestyle changes?
Absolutely! Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing stress, and getting regular exercise are all key lifestyle changes that can significantly improve digestive health and metabolic function.
Chapter 14 Digestive System And Body Metabolism
Conclusion
Understanding the interplay between the digestive system and body metabolism is fundamental to overall well-being. By adopting mindful eating habits, healthy lifestyle practices, and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can optimize your body’s remarkable ability to transform food into energy and essential nutrients.
Are you interested in learning more about the complexities of the digestive system and metabolism? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and let’s continue this exploration together!






