Imagine a world where a delicate balance of forces dictates the strength of an acid, where the presence of a seemingly unrelated ion can dramatically alter the equilibrium of a chemical reaction. This is the fascinating realm of the common ion effect, a phenomenon that plays a crucial role in understanding the ionization of acids and other chemical systems. While it may sound complex, exploring this concept unlocks a deeper understanding of chemistry, unraveling the intricacies of a world often invisible to the naked eye.
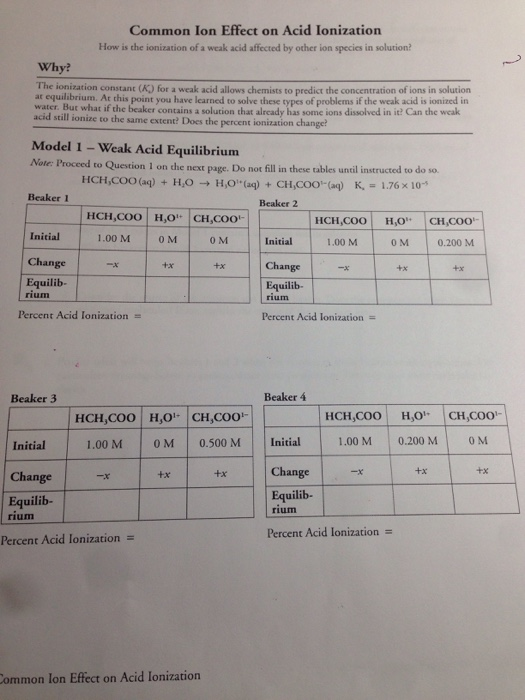
Image: justin-chapter.blogspot.com
The common ion effect, in essence, describes the suppression of ionization of a weak acid or base by the addition of a soluble salt containing a common ion. It provides a powerful tool for manipulating the extent of ionization and controlling the properties of solutions. This concept, seemingly abstract, has profound implications in various scientific fields, particularly in analytical chemistry, chemical engineering, and environmental science.
Delving into the Depths: Understanding the Common Ion Effect
To grasp the essence of the common ion effect, let’s delve into its core principles, starting with a relatable analogy. Imagine a crowded room, where people are constantly interacting. Now, imagine adding more individuals to the room, increasing the density of people. This increased density makes it harder for people to move freely, just as the presence of a common ion hinders the ionization of a weak acid.
In chemical terms, the common ion effect arises when a soluble salt containing an ion that is already present in a weak acid or base solution is added. This addition increases the concentration of the common ion, shifting the equilibrium of the ionization reaction to favor the formation of the undissociated acid or base.
To illustrate this principle, let’s consider the ionization of the weak acid, acetic acid (CH3COOH), in water.
CH3COOH(aq) <=> H+(aq) + CH3COO–(aq)
The addition of a common ion, such as acetate (CH3COO–), from a soluble salt like sodium acetate (CH3COONa), will push the equilibrium to the left, decreasing the concentration of H+ ions and effectively suppressing the ionization of acetic acid.
The Power of Le Chatelier’s Principle
The common ion effect beautifully aligns with Le Chatelier’s principle, a fundamental principle in chemistry stating that if a change in conditions is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift in a direction that relieves the stress. In the context of the common ion effect, the “stress” is the addition of a common ion, and the system shifts to minimize the impact of this stress by decreasing the ionization of the weak acid.
Practical Applications: From Chemistry Labs to Everyday Life
The common ion effect, far from being a mere theoretical concept, finds practical application in various fields. In analytical chemistry, it is used to control the solubility of sparingly soluble salts, enabling the selective precipitation of specific ions from a mixture. For instance, the addition of a common ion, such as chloride ions, to a solution containing silver ions can decrease the solubility of silver chloride, leading to its precipitation.
In chemical engineering, the common ion effect plays a crucial role in controlling pH in various industrial processes. By carefully adding common ions, engineers can optimize the pH of solutions, ensuring optimal reaction conditions and minimizing unwanted side reactions.
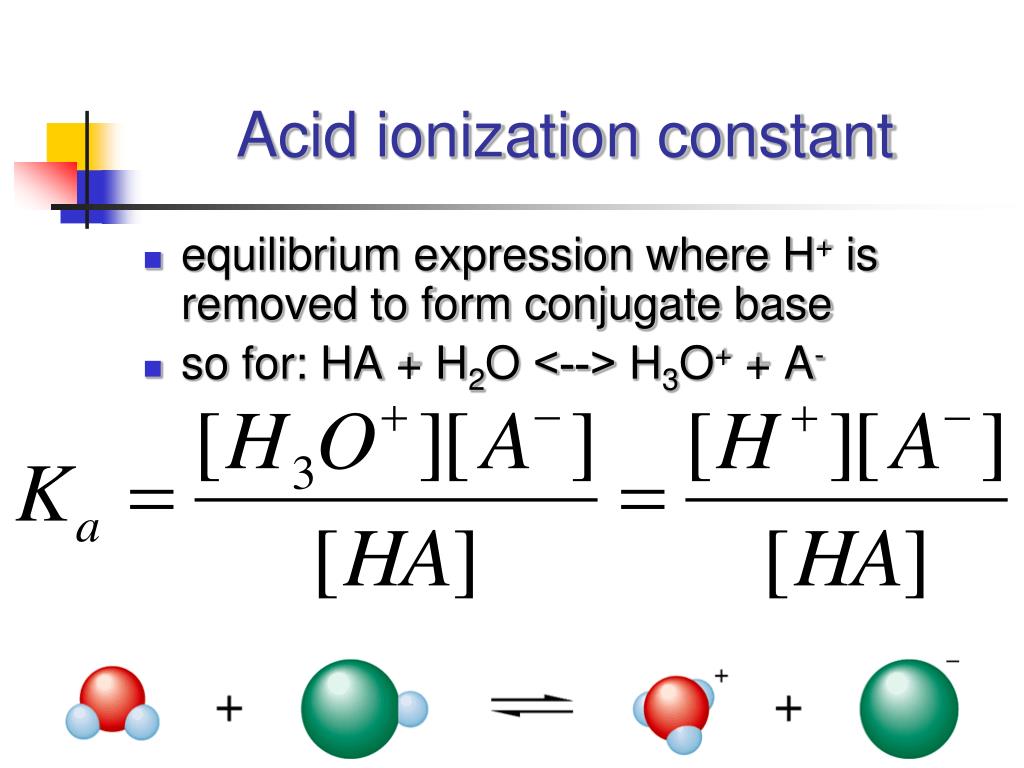
Image: www.slideserve.com
Impact on Acid Ionization: A Closer Look
The common ion effect profoundly influences the ionization of weak acids. As we explored earlier, the addition of a common ion suppresses ionization, making the weak acid even weaker. This effect is mathematically quantified using the acid dissociation constant (Ka), which represents the equilibrium constant for the ionization of a weak acid.
In the presence of a common ion, the concentration of the common ion appears in the denominator of the Ka expression, leading to a decrease in the overall Ka value. This lower Ka reflects the reduced ionization of the weak acid.
The common ion effect also plays a crucial role in buffer solutions, mixtures that resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. Buffer solutions typically consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The common ion effect helps maintain the pH within a specific range, making buffer solutions essential in biological systems, chemical analysis, and industrial processes.
Expert Insights: Unleashing the Power of the Common Ion Effect
Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned chemist and expert in chemical equilibrium, emphasizes the importance of understanding the common ion effect. “This effect is not just a theoretical curiosity; it has real-world implications, influencing everything from the behavior of pharmaceutical drugs to the effectiveness of agricultural fertilizers,” shares Dr. Carter.
Professor David Jones, a leading researcher in analytical chemistry, echoes this sentiment, highlighting the importance of the common ion effect in analytical techniques: “The common ion effect provides a powerful tool for selectively separating and analyzing ions in complex mixtures. By manipulating the concentration of common ions, we can control the solubility of ions, enabling precise and accurate analytical measurements.”
Navigating the Common Ion Effect: Actionable Tips for Students and Professionals
To effectively utilize the common ion effect, consider the following actionable tips:
- Master the Concepts: A thorough understanding of equilibrium principles and chemical reactions is crucial to successfully applying the common ion effect.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: Solving practice problems and working through examples helps solidify the concepts and empowers you to confidently apply them.
- Visualize the Process: Creating simple diagrams and representations of the equilibrium shifts caused by the addition of a common ion aids in visualizing this dynamic process.
- Leverage Online Resources: Numerous online tutorials, videos, and interactive simulations provide valuable resources for enhancing your understanding of the common ion effect.
Common Ion Effect On Acid Ionization Pogil
Conclusion: Empowering Your Understanding of Chemistry
The common ion effect, though a seemingly complex topic, unlocks a deeper understanding of chemical equilibrium and the behavior of acidic and basic solutions. By mastering this effect and its practical applications, you gain a powerful tool for navigating the intricacies of chemistry, from the depths of scientific research to the everyday world around us.
Embrace the challenge, explore its intricacies, and unlock the mysteries of the common ion effect, empowering your understanding of chemistry and the chemical world we inhabit.






