Have you ever wondered why a metal spoon heats up much faster than a wooden one when placed in a hot cup of coffee? Or why a pool of water takes so long to warm up on a sunny day? The answer lies in the fascinating world of specific heat and heat capacity. These concepts explain how different materials respond to the addition or removal of heat, influencing their temperature changes. This article delves into the realm of specific heat and heat capacity, exploring their definitions, applications, and the key to understanding those tricky worksheet answers.

Image: www.tes.com
Imagine a scenario where you’re preparing breakfast. You have a pan of water on the stove and a metal spatula to stir it. As you heat the water, you notice the spatula quickly becomes hot to the touch, while the water remains relatively cool. This difference in heating behavior is attributed to the distinct specific heat capacities of water and metal. This article aims to demystify these concepts, helping you master the art of tackling specific heat and heat capacity worksheets with confidence.
Understanding Specific Heat and Heat Capacity
Specific heat and heat capacity, while often used interchangeably, describe distinct aspects of a substance’s response to heat energy.
Specific Heat: A Material’s Thermal Inertia
Specific heat (often denoted as ‘c’) quantifies a substance’s resistance to temperature change. It represents the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius (or one Kelvin). For example, water has a high specific heat, implying it requires a considerable amount of heat energy to raise its temperature. This is why it takes longer to boil a pot of water than to heat up a piece of metal.
Heat Capacity: The Overall Heat Holding Ability
Heat capacity (often denoted as ‘C’), on the other hand, reflects the total amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of an entire object by one degree. It is influenced by both the specific heat of the substance and its mass. A larger object, even composed of the same material, will have a higher heat capacity due to its greater mass.
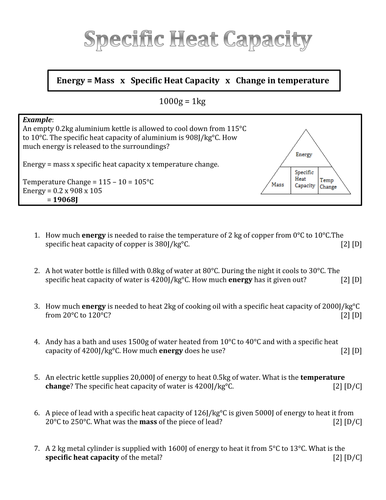
Image: lessonfullfrancie.z21.web.core.windows.net
Calculating Heat Transfer: The Q = mcΔT Equation
A fundamental equation in the study of heat transfer is the following:
Q = mcΔT
Where:
- Q represents the amount of heat energy transferred (in Joules).
- m signifies the mass of the object (in grams or kilograms).
- c denotes the specific heat of the substance (in J/g°C or J/kg°K).
- ΔT represents the change in temperature (in °C or °K), calculated as the final temperature minus the initial temperature.
This equation allows us to calculate the amount of heat energy required to raise or lower the temperature of a given object.
Applications of Specific Heat and Heat Capacity
The concepts of specific heat and heat capacity find widespread applications in various fields, including:
- Engineering: Engineers use these concepts to design engines, heat exchangers, and other thermal systems, optimizing their performance and efficiency.
- Climate Science: Understanding the specific heat of water is crucial for studying climate patterns and predicting global warming effects.
- Food Science: Specific heat knowledge is critical in the food industry for processes like cooking, freezing, and preserving foods.
- Biology: Specific heat plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature in living organisms. For example, water’s high specific heat helps maintain a stable internal temperature for humans.
Tackling Specific Heat and Heat Capacity Worksheets
When approaching specific heat and heat capacity worksheets, understanding the concept of heat transfer is key. Most worksheets will involve calculations using the Q = mcΔT equation. Here’s a breakdown of common problems and how to approach them:
1. Calculating Heat Energy:
The most basic type of problem involves calculating the amount of heat energy required to raise or lower the temperature of an object. To do this, you need to know the object’s mass, specific heat, and the temperature change.
2. Determining Specific Heat:
Some problems will require you to calculate the specific heat of a substance. This involves knowing the mass, heat energy, and temperature change of the substance.
3. Solving for Temperature Change:
In other scenarios, you might have to determine the temperature change that occurs when a specific amount of heat energy is added or removed from a substance.
Tips for Conquering Specific Heat and Heat Capacity Worksheets
Here are some useful tips to help you ace those specific heat and heat capacity worksheets:
- Know Your Units: Ensure you use consistent units for mass (grams or kilograms), temperature (Celsius or Kelvin), and heat energy (Joules).
- Practice, Practice, Practice: Solving numerous practice problems is the best way to solidify your understanding of the concepts.
- Visualize the Process: Try to visualize the heat transfer occurring in the problem scenario. This can help you understand the direction of heat flow and the resulting temperature changes.
- Check Your Answers: Always double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
Remember, mastering specific heat and heat capacity worksheets involves a combination of understanding the concepts, mastering the Q = mcΔT equation, and practicing problem-solving skills. With consistent effort and a bit of practice, you’ll be able to confidently solve even the most challenging questions.
Specific Heat and Heat Capacity FAQs
Q: What is the difference between specific heat and heat capacity?
A: Specific heat measures a substance’s resistance to temperature change per unit mass, while heat capacity measures the total amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of an entire object by one degree.
Q: What are some common units used for specific heat and heat capacity?
A: Common units for specific heat include J/g°C or J/kg°K. Heat capacity is typically measured in J/°C or J/°K.
Q: How does specific heat affect the rate at which a substance heats up or cools down?
A: Substances with high specific heat require more energy to change their temperature, so they heat up and cool down more slowly. Those with low specific heat heat up and cool down faster.
Q: Can you give an example of how specific heat is relevant in everyday life?
A: Water’s high specific heat is the reason why oceans moderate coastal temperatures, preventing extreme fluctuations.
Q: What are some real-world applications of heat capacity?
A: Heat capacity plays a crucial role in designing thermal systems like car engines, power plants, and solar panels.
Specific Heat And Heat Capacity Worksheet Answers
Conclusion
Specific heat and heat capacity are fundamental concepts in thermodynamics, describing a substance’s ability to store and transfer thermal energy. By understanding these concepts and mastering the Q = mcΔT equation, you can confidently tackle specific heat and heat capacity worksheets. Remember, practice makes perfect, so keep working at it, and you’ll soon be an expert in heat transfer.
Are you interested in learning more about specific heat and heat capacity? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below! Let’s continue the discussion and explore the fascinating world of thermal energy together!






