Remember that first chemistry class in high school, the one where you learned about atoms and their tiny, invisible world? It was fascinating, right? Trying to visualize those protons, neutrons, and electrons swirling around like planets in a solar system. And then came the concept of isotopes, which, honestly, initially felt like a whole new level of complexity. I’ll admit, I didn’t fully grasp the concept of isotopes until I got my hands on a worksheet and started working through the problems. It was like unlocking a new piece of the puzzle, a way to understand the variations within the basic atom. If you’re also looking for a bit of help deciphering the world of atoms and isotopes, this guide is here to shed light on the key concepts and provide a comprehensive answer key to those worksheet challenges.
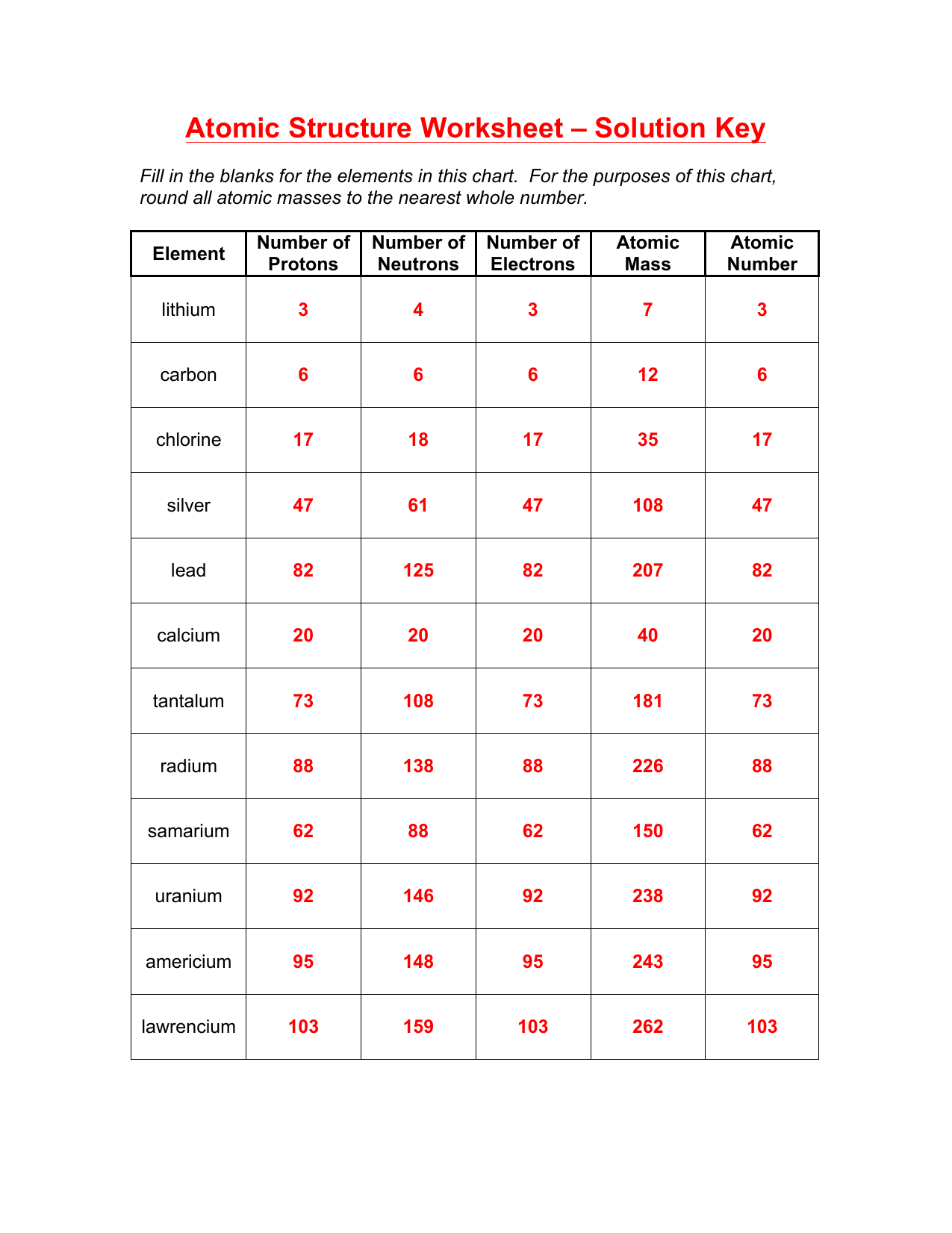
Image: lessondbjonathan.z21.web.core.windows.net
This article is a comprehensive explanation of atoms and isotopes. It will address the fundamental concepts, answer common questions, and provide a comprehensive answer key to help you understand the topic in detail. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of atoms and their variations.
Understanding the Basics of Atoms
The Building Blocks of Matter
Atoms are the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Imagine them as the tiny building blocks of everything you can see and touch – from your phone to the air you breathe. But these building blocks are incredibly small, so small they can’t be seen even with the most powerful microscopes. Instead, we rely on our understanding of atomic structure, the arrangement of particles within the atom, to understand how they work.
The Parts of an Atom
At the center of every atom sits the nucleus. This tiny dense core holds two types of particles: protons and neutrons. Protons carry a positive charge, while neutrons are neutral, carrying no charge. Whizzing around the nucleus are electrons, particles with a negative charge. These electrons exist in a cloud-like region called the electron cloud, where they are attracted to the positively charged nucleus.

Image: learninglibraryverla.z13.web.core.windows.net
The Importance of the Atomic Number
Each element is defined by its atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. For example, all hydrogen atoms have one proton, giving them an atomic number of 1. All oxygen atoms have eight protons, giving them an atomic number of 8. This number is unique to each element and acts as a signature, identifying it from every other element.
Exploring the World of Isotopes
Variations Within the Atom: Isotopes
While all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, they don’t always have the same number of neutrons. These variations are called isotopes. Think of them like the different flavors of a certain cookie: they’re all the same basic cookie, but they have a slight difference in ingredients, giving them a unique characteristic.
The Influence of Neutrons
The number of neutrons in an atom is known as the neutron number. When you add the number of neutrons and protons together, you get the atomic mass number. Isotopes of the same element differ in their neutron number, meaning they have different atomic mass numbers. This variation in neutron count doesn’t change the element’s identity because it still has the same number of protons, but it does affect its properties.
Everyday Examples of Isotopes
You might be surprised to learn that isotopes are all around us. Carbon-14, with eight neutrons, is a radioactive isotope used in carbon dating to determine the age of ancient artifacts and even fossils. Another example is the isotope uranium-235, which is used as fuel for nuclear power plants. These different forms of the same element have unique properties that make them valuable in various applications.
Applications of Isotopes and their Importance
Unlocking the Secrets of the Past: Carbon Dating
Isotopes play a vital role in understanding the past. For instance, carbon-14 dating is a widely used technique in archaeology and paleontology. The principle is based on the radioactive decay of carbon-14, an isotope of carbon. The technique allows scientists to determine the age of ancient bones, artifacts, and even fossils, offering a glimpse into the deep history of our planet.
Powering the Future: Nuclear Energy
Isotopes are central to nuclear energy production. Some isotopes, like uranium-235, are highly radioactive and undergo nuclear fission, releasing large amounts of energy. This energy can be harnessed to generate electricity, offering a valuable alternative energy source. Nuclear energy is a topic of ongoing debate, but there’s no denying the role isotopes play in this significant field.
Medical Advancements: Radioactive Isotopes
Isotopes are used extensively in the medical field, particularly radioactive isotopes. These isotopes are incorporated into drugs or tracers, allowing doctors to visualize organs and tissues, diagnose diseases, and monitor treatments. Radioactive isotopes have revolutionized medical imaging techniques like PET scans, ensuring more efficient and accurate diagnoses and treatments.
Tips for Mastering Atoms and Isotopes
Embrace Visualization
Visualizing atomic structure can greatly aid understanding. You can create simple diagrams, use online interactive models, or even build physical models to represent atoms and isotopes.
Practice with Worksheets and Problems
Like any new concept, practice is key to mastering atoms and isotopes. Solve worksheets, answer practice questions, and work through problem sets to reinforce the ideas. Don’t be afraid to ask for help when you get stuck – that’s how you learn and grow.
FAQs about Atoms and Isotopes
Q: What are the key differences between atoms and isotopes?
A: Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of an element, defined by their atomic number (number of protons). Isotopes are variations of the same element, differing only in their neutron count (and therefore their atomic mass number).
Q: How do isotopes affect the properties of an element?
A: The change in neutron number can slightly affect the mass and properties of an element. For example, radioactive isotopes like carbon-14 decay at a predictable rate, allowing for carbon dating.
Q: What are some common applications of isotopes?
A: Isotopes have a wide range of applications. Carbon-14 is used for carbon dating ancient artifacts, uranium-235 is used as fuel in nuclear power plants, and radioactive isotopes are used in medical imaging techniques.
Q: Are all isotopes radioactive?
A: No, not all isotopes are radioactive. Some isotopes are stable, meaning they do not undergo radioactive decay. However, some isotopes are radioactive, meaning their nuclei are unstable and decay, releasing particles and energy.
Q: How can I learn more about atoms and isotopes?
A: You can find a wealth of information online, in textbooks, and through educational videos. Many universities and science museums also offer interactive exhibits and workshops on atomic structure and isotopes.
Atoms And Isotopes Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion and Call to Action
Understanding atoms and isotopes is fundamental to grasping the world around us. From the ancient past to the future of energy, these tiny particles play a vital role in shaping our world. By exploring the principles of atomic structure, the variations within the atomic world, and the applications of isotopes, we can gain a deeper understanding of the invisible universe that makes up our reality.
Are you curious to learn more about atoms and isotopes? Do you have any questions about this fascinating topic? Let me know in the comments below, and let’s embark on this exciting journey of scientific discovery together!






