Have you ever wondered why some chemical reactions release energy, like the burning of fuel, while others require energy to proceed, like photosynthesis? The answer lies in the concept of bond energy, a fundamental principle in chemistry that governs the stability and reactivity of molecules.

Image: worksheetdbopioid.z21.web.core.windows.net
This article delves into the fascinating world of bond energy, using Chem Worksheet 16.2 as a guide. We’ll explore how understanding bond energy can help predict the enthalpy change of chemical reactions, analyze the strength of chemical bonds, and ultimately unlock the secrets behind the behavior of molecules.
Bonds, Energy, and Stability
Imagine atoms as Lego blocks, each with tiny hooks called “bonds” that allow them to join together. The strength of these “hooks” determines how strongly the blocks are connected, impacting the stability and reactivity of the resulting structures. In chemistry, these “hooks” are called chemical bonds, and their strength is measured by bond energy.
Bond energy represents the amount of energy required to break one mole of a specific type of bond in the gaseous state, measured in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol). Think of it as the amount of energy needed to pull apart those Lego blocks, breaking the connection between them. The stronger the bond, the higher the bond energy, and the more energy required to break it.
Bond energy is a crucial concept in chemistry because it allows us to understand the energetics of chemical reactions. When bonds are broken, energy is absorbed, while the formation of new bonds releases energy. By analyzing the bond energies involved in a reaction, we can predict whether it will be exothermic (releases heat) or endothermic (absorbs heat).
Exploring Bond Energy in Chem Worksheet 16.2
Let’s take a closer look at Chem Worksheet 16.2, which focuses on applying the concept of bond energy to calculate the enthalpy change of reactions. This worksheet typically involves two key steps:
1. Identifying and Analyzing Bonds
The first step involves carefully analyzing the chemical equation and identifying all the bonds present in the reactants and products. This requires familiarity with chemical structures and bond types, such as single, double, and triple bonds. You’ll need to know the bond energy values for each of these bonds, which can be found in tables or provided in the worksheet.
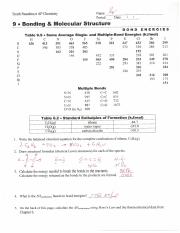
Image: classlibrarypfeifer.z13.web.core.windows.net
2. Calculating the Enthalpy Change
Once you’ve identified all the bonds, the next step is to calculate the total bond energy of the reactants and products. This is done by multiplying the bond energy of each type of bond by its frequency in the molecule. For example, if a molecule has two C-H bonds and each has a bond energy of 413 kJ/mol, the total contribution of C-H bonds would be 826 kJ/mol (2 bonds * 413 kJ/mol/bond).
The enthalpy change (ΔH) of the reaction is then calculated using the following equation:
If ΔH is negative, the reaction is exothermic and releases energy. If ΔH is positive, the reaction is endothermic and requires energy to proceed.
Real-World Applications of Bond Energy
Beyond the confines of chemistry textbooks, bond energy has far-reaching applications in various fields:
- Fuel Chemistry: Understanding bond energies helps us analyze the combustion of fuels like gasoline and natural gas. Knowing the bond energies of the C-H bonds in hydrocarbons helps determine the efficiency and heat released during combustion.
- Materials Science: Bond energies are crucial in designing and developing new materials. The strength and stability of materials, such as plastics and ceramics, are directly related to the bond energies of the molecules within them.
- Biochemistry: From the intricate workings of enzymes to the structure of DNA, bond energies play a pivotal role in biological processes. Understanding bond energies allows us to analyze enzyme activity, protein folding, and DNA replication.
Beyond the Worksheet: Exploring Further
Chem Worksheet 16.2 provides a solid foundation for understanding bond energy. Yet, the world of chemistry is vast, and there’s much more to explore!
To delve deeper into the complexities of bond energy, consider exploring these avenues:
- Advanced Chemistry Textbooks: Textbooks specializing in physical chemistry and organic chemistry delve into the theoretical underpinnings of bond energy and its applications in various chemical systems.
- Scientific Journals: Numerous scientific journals publish research articles on bond energy, covering advancements in theoretical calculations, experimental techniques, and real-world applications.
- Online Resources: Websites like Khan Academy and Chemistry LibreTexts offer valuable resources and interactive simulations for learning about bond energy and related concepts.
Bond Energy Chem Worksheet 16 2
Conclusion
By understanding bond energy, a fundamental concept in chemistry, we gain valuable insights into the behavior of molecules and the energetics of chemical reactions. Chem Worksheet 16.2 serves as a starting point for delving into this intriguing topic, providing a practical framework for calculating the enthalpy change of reactions. As you explore this concept further, you’ll find that bond energy holds the key to unraveling the mysteries behind chemical reactions and the countless applications they have in our world.






