Remember that awkward moment in biology class when your teacher threw a cladogram at you and expected you to decipher its tangled branches? I certainly do. I stared at the diagram, a jumble of lines and labels, feeling utterly lost. What were those little boxes called “nodes?” What were the characteristics they represented? And how on earth did I figure out which organism was most closely related to which? Thankfully, my teacher, a patient soul, walked me through it, explaining how cladograms reveal the evolutionary history of life. That experience ignited my fascination with these fascinating diagrams. Today, I’m here to guide you through the world of cladogram analysis, helping you unlock the secrets of evolutionary relationships.

Image: worksheetzone.org
Cladograms, like cryptic puzzles, hold the key to understanding the evolutionary journey of organisms. They’re visual representations of how species are related, stemming from a common ancestor. Every branch on a cladogram speaks volumes about shared characteristics and the evolutionary paths taken by these organisms. Decoding these evolutionary narratives is what makes cladogram analysis so intriguing.
What is Cladogram Analysis?
Cladogram analysis is a powerful tool used in biology to reconstruct evolutionary relationships between organisms. It’s essentially the art of creating and interpreting cladograms, those branching diagrams you might have seen in textbooks or biology labs.
Imagine a family tree, but instead of tracing your ancestry through generations, you’re tracing the lineage of different species. A cladogram works like this: it starts with a common ancestor at the base and branches out, representing the evolution of different species over time. Each branch point, known as a “node,” reflects the emergence of a new trait, or derived character, that sets apart the descendants from their shared ancestor.
Diving Deeper into the Basics
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements of a cladogram:
- Root: The base of the cladogram, representing the common ancestor for all the organisms being compared.
- Branches: Lines connecting different organisms and nodes, illustrating evolutionary lineages.
- Nodes: Branching points on the cladogram where a new trait (a derived character) emerged, splitting the lineage into two or more groups.
- Derived Characters: These are the traits that distinguish one group from another. They are the key to understanding evolutionary relationships.
- Taxa: The specific groups of organisms (like species or genera) being compared in the cladogram. They are placed at the tips of the branches.
The Power of Shared Traits
The core principle of cladogram analysis lies in identifying shared derived characters, also known as synapomorphies. These are traits that are unique to a particular group of organisms and their descendants. By comparing presence and absence of these derived characters, scientists can determine the evolutionary relationships between different species.
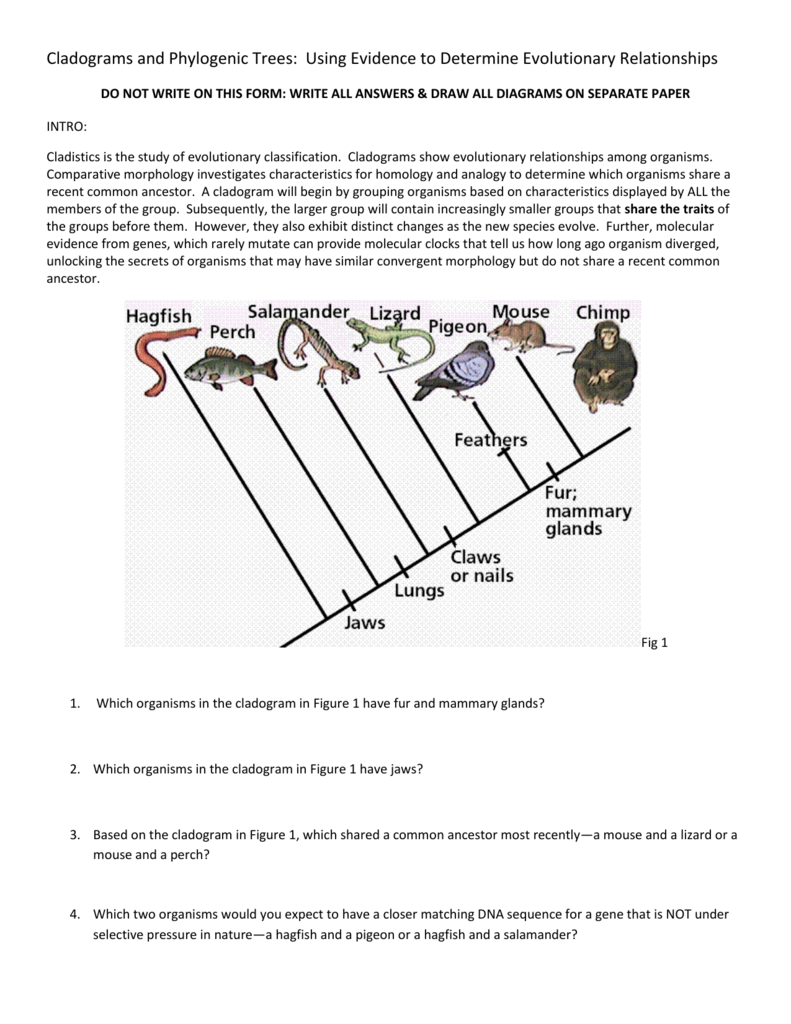
Image: stewcomtose.weebly.com
How are Cladograms Constructed?
To construct a cladogram, biologists gather data on a range of organisms, focusing on anatomical, molecular (DNA or RNA), or behavioral traits. They then identify shared derived characters, carefully analyzing which traits emerged at specific points in evolutionary history. Using these insights, they assemble the branches of the cladogram, representing the evolutionary divergence of organisms based on their shared history.
Decoding the Evolutionary Blueprint
Cladograms are not simply static diagrams; they offer a dynamic window into the evolutionary history of life. By studying the branching patterns and shared traits, we can learn about:
- Phylogeny: The evolutionary history of a group of organisms, highlighting their ancestor-descendant relationships.
- Time Scale: Although not always directly depicted, cladograms provide insights into the relative timing of evolutionary events.
- Adaptive Changes: The emergence of new traits at different nodes represents adaptations that enabled organisms to thrive in specific environments.
Evolutionary Insights for a Changing World
The study of cladograms has undergone continuous development, with modern advancements enabling more complex and accurate analyses. The use of molecular data, particularly DNA and RNA sequences, has revolutionized our understanding of evolutionary relationships. These advancements are constantly revealing new insights into the intricate web of life. Scientists are using cladogram analysis to uncover:
- Emerging Diseases: Researchers can analyze the evolutionary history of pathogens, like viruses and bacteria, to understand how they emerge and spread, leading to better prevention and treatment strategies.
- Conservation Efforts: By understanding evolutionary relationships, scientists can prioritize conservation efforts for endangered species, ensuring the preservation of biodiversity.
- Development of Pharmaceuticals: Cladogram analysis is now instrumental in understanding the evolutionary history of genes and proteins, leading to the development of new drugs and treatments.
Tips for Mastering Cladogram Analysis
Whether you’re a student tackling a biology assignment or a curious learner exploring the world of evolution, understanding how to analyze a cladogram can be rewarding. Here are some valuable tips:
- Start Simple: Begin with basic cladograms focusing on a small number of organisms and traits. Grasp the fundamental principles before moving on to more complex examples.
- Focus on Derived Characters: Carefully identify the traits that distinguish different groups. These are the crucial clues that unravel the evolutionary relationships.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Work through various cladogram analysis exercises to solidify your understanding of the process. The more you practice, the more confident you’ll become.
- Use Online Resources: Explore interactive cladogram tools and websites that offer visual representations and exercises. They provide a dynamic learning experience.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Ask Questions: Seek clarification from your teacher, tutor, or online resources whenever you encounter a confusing element.
Key to Unlock the Answers
Understanding the principles of cladogram analysis is a crucial step in mastering evolutionary biology. This knowledge will equip you with the tools to decipher the intricate evolutionary history of organisms, from microscopic bacteria to majestic whales. Just remember to start with the basics, focus on derived characters, and practice your analysis skills. Remember: the journey of understanding evolution is a rewarding one, filled with fascinating discoveries and a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
FAQ
Q: What are the benefits of using cladogram analysis?
A: Cladogram analysis offers several valuable benefits:
- Revealing Phylogeny: It helps us understand the evolutionary relationships and ancestry of organisms.
- Identifying Adaptive Traits: It highlights the development of new traits that enabled organisms to thrive in diverse environments.
- Supporting Evolutionary Theory: It provides strong evidence for the process of evolution through natural selection.
Q: How does cladogram analysis differ from phylogenetic trees?
A: While cladograms and phylogenetic trees both depict evolutionary relationships, there’s a key difference:
- Cladograms: Focus primarily on branching patterns and the relationships between organisms, not necessarily the exact time scale of evolutionary events.
- Phylogenetic Trees: Often depict the evolutionary timeline, with branch lengths representing the time elapsed since divergence.
Q: What are some real-world applications of cladogram analysis?
A: Cladogram analysis plays a vital role in various fields:
- Medicine: Understanding the evolution of pathogens like viruses and bacteria helps in developing treatments and vaccines.
- Conservation Biology: It informs conservation efforts by identifying evolutionary relationships and identifying vulnerable species.
- Biotechnology: It aids in understanding the evolutionary history of genes and proteins, leading to advancements in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
Answer Key Cladogram Analysis Worksheet Answers
Interested in Unveiling Evolutionary Mysteries?
If you found this exploration of cladograms intriguing, I encourage you to delve deeper! Explore online resources, consider taking a biology course, or even explore research papers on specific topics that pique your interest. The field of evolutionary biology is a dynamic and ever-evolving realm, offering endless opportunities for discovery and understanding.






