Imagine stepping into a bustling marketplace, vibrant with life, yet beneath the surface, you sense a quiet desperation. Mothers struggle to afford nutritious food for their children, young men struggle to find work, and a sense of fear lingers in the air due to a lack of access to healthcare. This is the reality of many communities, and it’s the very essence of what community health nurses grapple with every day. They understand that health is not merely the absence of disease, but the well-being of individuals and the thriving of the community as a whole. This is where the concept of community diagnosis comes in.

Image: www.researchgate.net
Community diagnosis is the process of systematically assessing the health status of a community – its strengths, weaknesses, and health risks – to identify priority health concerns and develop effective interventions. It’s not merely about collecting data but understanding the intricate web of social, economic, and environmental factors that contribute to a community’s health outcomes. In essence, it’s about understanding the community’s story to write a better future for its residents.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Community Diagnosis
The Purpose and Scope
Community diagnosis is more than just collecting statistics; it’s about painting a holistic picture of the community’s health. It encompasses several crucial elements:
- Identifying health problems: This involves pinpointing the specific health issues that affect the community and their prevalence. For instance, a diagnosis might reveal a high rate of obesity, infant mortality, or limited access to mental health services.
- Analyzing the causes: Beyond identifying problems, understanding the underlying contributing factors is essential. This could involve exploring social, environmental, economic, or political factors that impact the health of the community. For example, a community with a high rate of obesity might have limited access to healthy food options or have cultural influences that promote unhealthy eating habits.
- Determining the community’s strengths: Every community has its strengths, often hidden beneath the surface. Identifying existing community resources, social networks, and resilient individuals is vital for planning efficient interventions. For instance, a community might have a strong network of social support or a thriving community garden, which can be leveraged to address health problems.
- Planning interventions: This involves translating the findings from the community diagnosis into actionable solutions. The process involves utilizing the identified strengths to develop effective healthcare programs, resource allocation, and community empowerment initiatives.
The Key Players: Community Health Nurses
Community health nurses are the champions of community diagnosis. They are the bridge between the community and the healthcare system, acting as health educators, advocates, and problem-solvers. They possess the knowledge, skills, and compassion to navigate the complexities of community health. Their roles encompass:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Community health nurses use a variety of tools and techniques to collect data, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, and even ecological mapping. This data is then analyzed to identify patterns and trends that highlight the community’s health profile.
- Community Engagement: Building trust and rapport with community members is paramount. Nurses actively listen to residents’ concerns, understand their needs, and involve them in decision-making processes. This collaborative approach ensures that interventions are tailored to the community’s specific needs and priorities.
- Resource Navigation and Advocacy: Community health nurses act as navigators, connecting communities with the resources they need to improve their health. This might involve facilitating access to healthcare services, connecting residents with social support programs, or advocating for policies that promote health equity.
- Program Development and Implementation: Nurses work collaboratively with community members, local organizations, and other healthcare providers to develop and implement interventions that address the identified health concerns. These might include health education programs, community gardens, or support groups for individuals facing specific health challenges.
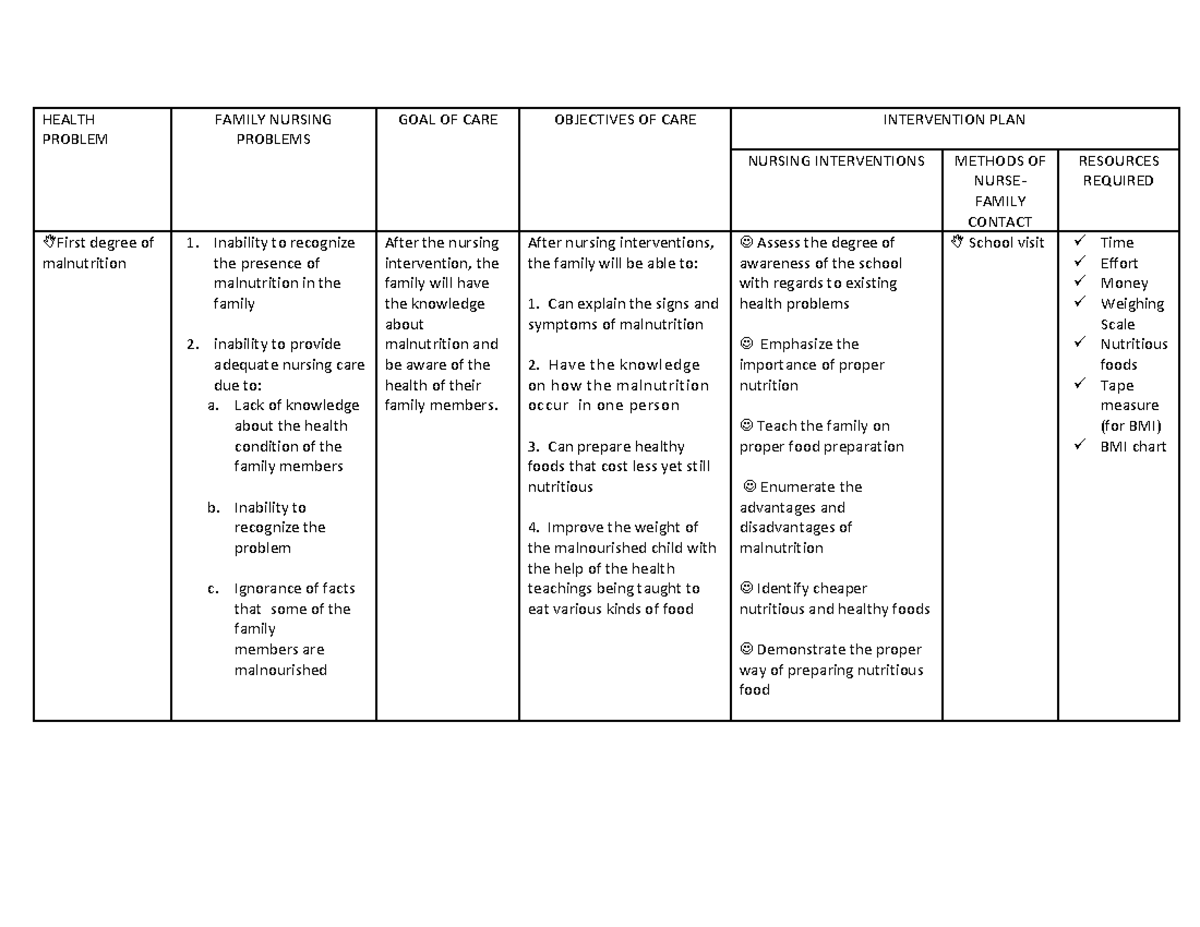
Image: www.studocu.com
Steps to Conduct a Community Diagnosis
1. Defining the Community
The first step involves clearly defining the community to be assessed. This could be a geographic region, a specific population group, or a defined neighborhood within a larger city. Defining parameters allows for focused data collection and targeted interventions.
2. Gathering Data
Community health nurses utilize various methods to gather data, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the community’s health status:
- Primary Data: This involves directly collecting data from community members through surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observations. This method provides valuable insights into the community’s perspectives, experiences, and needs.
- Secondary Data: This involves utilizing existing data sources such as vital statistics, health records, demographic data, and environmental reports. This method provides a broader context and can reveal historical trends that can inform interventions.
- Ecological Mapping: This involves visually mapping community resources, infrastructure, and environmental factors that influence health. It helps identify geographical disparities, access to healthcare facilities, and environmental hazards that impact health outcomes.
3. Analyzing and Interpreting Data
Once data is collected, the next step involves analyzing and interpreting it to identify patterns, trends, and potential contributing factors to health issues. This step often involves identifying key health indicators, mapping health data against demographic information, and understanding the social determinants of health that impact the community.
4. Developing a Community Health Profile
The analysis leads to the development of a community health profile, a comprehensive snapshot of the community’s health status. This document summarizes the key findings of the diagnosis, including the identified health problems, their contributing factors, the community’s strengths, and potential areas for intervention. This profile forms the foundation for developing effective and targeted interventions.
5. Prioritizing Health Concerns
Not all health problems require immediate attention. The community health profile guides nurses in prioritizing health concerns based on their severity, prevalence, impact on the community, and potential for intervention. This process ensures that resources are allocated effectively and interventions address the most pressing issues.
6. Developing Interventions
The final step involves translating the diagnosis into actionable interventions. This is a collaborative process involving community members, local stakeholders, and healthcare providers. Effective interventions are tailored to the community’s specific needs, strengths, and resources. Interventions might include:
- Health Education Programs: Providing information and education about health issues, prevention strategies, and healthy lifestyle choices. This could involve workshops, seminars, or community outreach programs.
- Health Promotion Initiatives: Working to create supportive environments that promote healthy behaviors. This might involve establishing community gardens, promoting physical activity in public spaces, or advocating for policies that promote health equity.
- Access to Care Programs: Connecting community members with healthcare services, including primary care, mental health services, and preventative screenings. This might involve establishing mobile clinics, organizing transportation services, or navigating complex healthcare systems.
- Community Empowerment Projects: Supporting and empowering communities to take ownership of their health. This might involve developing leadership programs, facilitating community-based participatory research, or building capacity within community organizations.
The Importance of Community Diagnosis in Community Health Nursing
Community diagnosis is a powerful tool for community health nurses, enabling them to effectively address the unique health needs of their communities. It provides a framework for:
- Identifying Gaps and Priorities: By understanding the community’s health status, nurses can pinpoint areas where services are lacking and prioritize interventions that address the most critical health concerns.
- Facilitating Resource Allocation: Community diagnosis provides evidence-based justification for requesting funding and allocating resources strategically to ensure interventions have the greatest impact.
- Building Community Partnerships: The process of conducting a community diagnosis fosters collaboration and builds trust within the community. It empowers residents to become advocates for their own health and actively engage in improving the overall well-being of their community.
- Addressing Health Disparities: Community diagnosis helps identify disparities in health outcomes within a community, allowing nurses to target interventions to underserved populations and promote health equity.
- Evaluating Program Effectiveness: The data collected during the community diagnosis process can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of implemented interventions and make necessary adjustments to improve their impact.
Community Diagnosis In Community Health Nursing
The Future of Community Diagnosis
The field of community diagnosis is constantly evolving, incorporating new technologies and approaches. Some of the emerging trends include:
- Data-driven decision-making: Utilizing big data analytics, machine learning, and predictive modeling to identify health trends and inform interventions more effectively.
- Mobile health (mHealth) technologies: Employing mobile devices and applications to facilitate data collection, health education, and communication within communities.
- Community-based participatory research: Empowering community members to participate in research projects that directly affect their health and well-being.
- Focus on social determinants of health: Recognizing the profound impact of social, environmental, and economic factors on health outcomes and incorporating these factors into community diagnosis and intervention planning.
Community diagnosis is a critical component of community health nursing, empowering nurses to act as champions of their communities’ health. By understanding the intricate web of factors that influence health outcomes, nurses can tailor interventions, mobilize resources, and build partnerships that create thriving communities, where every member has the opportunity to flourish.






