Ever felt overwhelmed during a patient assessment? Trying to remember every single detail, from their overall appearance to the tips of their toes, can feel like traversing a labyrinth. But fear not, fellow healthcare professionals! We’ve got the ultimate cheat sheet to navigate the head-to-toe assessment process with confidence and efficiency.

Image: www.pinterest.com
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to perform a thorough and accurate head-to-toe assessment. We’ll delve into each body system, outlining key areas to focus on, vital signs to monitor, and potential indicators of underlying health conditions. Whether you’re a seasoned nurse or a student just entering the medical field, this cheat sheet will be your trusted companion in the world of patient care.
Navigating the Body
The head-to-toe assessment is a methodical approach to patient evaluation, systematically examining each body system to identify any deviations from normal. It’s a crucial part of patient care, allowing healthcare providers to pinpoint potential health issues, assess their severity, and develop appropriate treatment plans. This comprehensive assessment is often conducted during the initial patient encounter, as well as at regular intervals during their stay or follow-up appointments.
The Head
General Appearance
Start by observing the patient’s general appearance, noting any immediate signs that might require attention. Consider factors like:
- Level of Consciousness: Are they alert and responsive, drowsy, or unconscious? This provides a quick insight into their mental status.
- Facial Expressions: Pay attention to their facial expressions. Do they appear distressed, in pain, or anxious? This can be a valuable indicator of their emotional state or potential underlying health issues.
- Posture: Are they sitting upright, slumped, or restricted in their movements? Their posture can offer clues about their comfort level, muscle strength, or potential pain.
- Skin Color: Note the overall skin color. Is it healthy, pale, flushed, or cyanotic? Any changes in skin color might indicate problems with oxygenation or circulation.
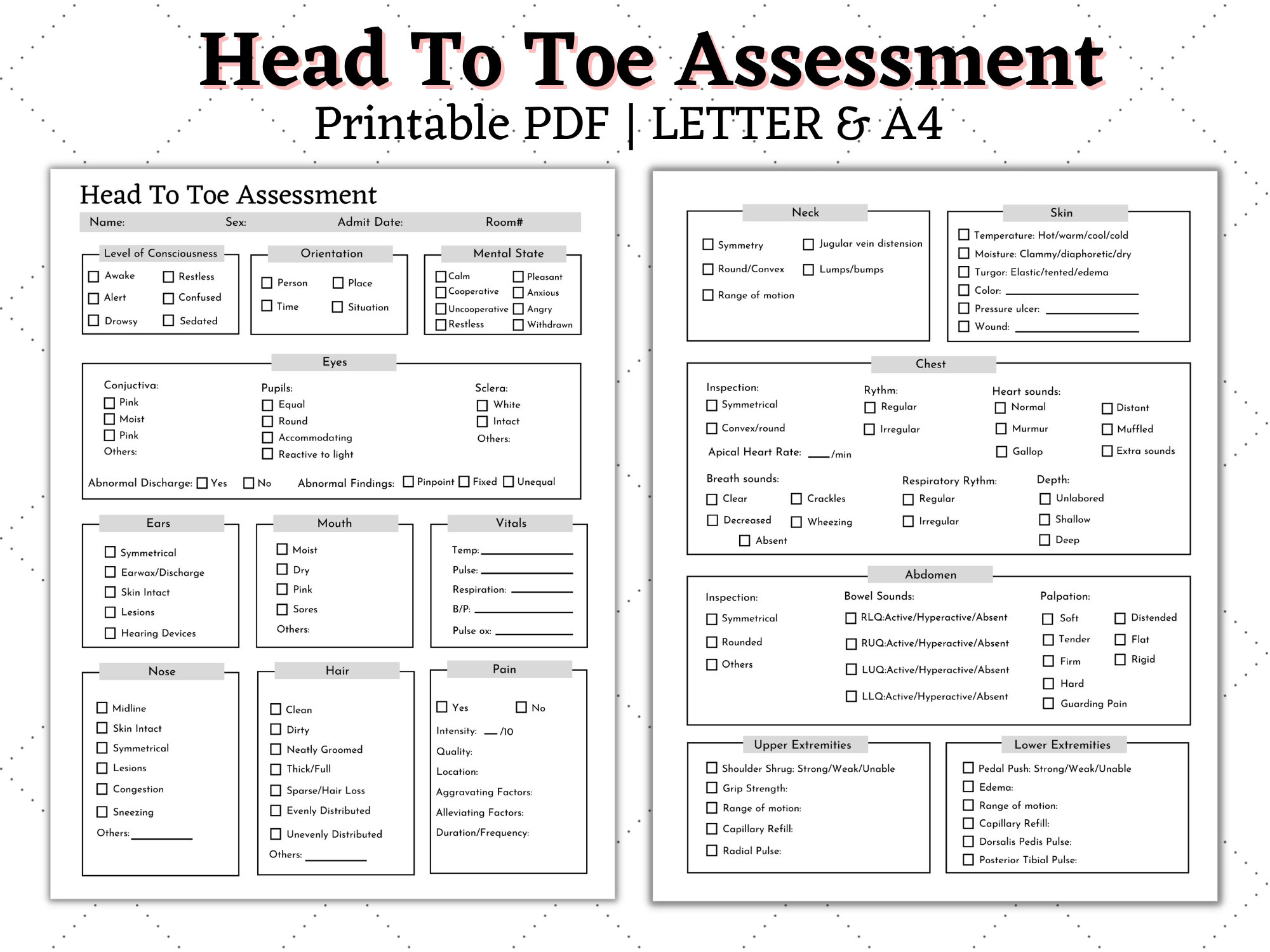
Image: forms.utpaqp.edu.pe
Head and Neck
Moving on to the head and neck, focus on:
- Head: Inspect the scalp for any lesions, bumps, or signs of hair loss. Feel for any tenderness or abnormalities.
- Eyes: Assess pupillary response to light, check for eye movement, and observe for any redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Ears: Inspect the ears for any inflammation or discharge. Check for tenderness upon palpation.
- Nose: Look for any signs of nasal discharge, redness, or deformities. Check for patency of the nostrils.
- Mouth: Examine the mouth for any sores, ulcers, or abnormalities. Observe the tongue for color, size, and movement. Check the teeth for alignment and any dental problems.
- Neck: Feel for any enlarged lymph nodes, assess the range of motion, and check for tenderness in the neck muscles.
- Trachea: Feel the trachea for midline position, ensuring it’s not deviated.
The Thorax
Respiratory System
The thorax houses the lungs, so pay close attention to any signs of respiratory distress:
- Respiratory Rate: Count their breaths per minute, noting any irregular patterns or labored breathing.
- Breath Sounds: Use a stethoscope to listen to their lungs. Are there any crackling sounds (rales), wheezing sounds (wheezes), or diminished breath sounds in any areas?
- Oxygen Saturation: Obtain their SpO2 reading using a pulse oximeter, aiming for a reading of 95% or higher.
- Chest Excursion: Observe the symmetry of chest expansion during breathing.
Cardiovascular System
The heart lies within the thorax, making it a key area for assessment:
- Heart Rate: Measure their pulse rate, noting any irregularities such as tachycardia (rapid heartbeat) or bradycardia (slow heartbeat).
- Blood Pressure: Obtain a blood pressure reading, monitoring for hypertension (high blood pressure) or hypotension (low blood pressure).
- Heart Sounds: Listen to their heart using a stethoscope. Are there any murmurs, gallops, or abnormal heart sounds?
The Abdomen
Inspection and Palpation
The abdomen is a complex region containing various organs. Begin with visual inspection, followed by palpation:
- Appearance: Observe the abdomen for any distention, scars, or masses.
- Auscultation: Use a stethoscope to listen for bowel sounds in all four quadrants.
- Palpation: Gently palpate the abdomen, starting with light pressure and gradually increasing. Note any tenderness, masses, or organ enlargement.
Gastrointestinal System
The GI tract is a major focus during abdominal assessment, considering:
- Bowel Movements: Ask about their bowel movements, noting the frequency, consistency, and any changes.
- Abdominal Pain: Inquire about any abdominal pain, its location, character, and any associated symptoms.
Genitourinary System
The genitourinary system is also significant in abdominal assessment. Inquire about:
- Urinary Frequency: Ask about their urine frequency and any changes in urination patterns.
- Urinary Incontinence: Inquire about any urinary incontinence or urinary tract infections (UTIs).
The Musculoskeletal System
From head to toe, assess the musculoskeletal system, paying attention to:
- Muscle Strength: Test their muscle strength in all extremities by asking them to perform simple movements like lifting their arms or squeezing your hand.
- Range of Motion: Assess their joint mobility in all limbs. Ask them to move their joints through their full range of motion. Note any pain, limitations, or crepitus (grating sounds).
- Skeletal Integrity: Inspect their bones for any deformities, fractures, or tenderness.
The Integumentary System
Finally, assess the skin, a vital part of the body’s protective barrier:
- Skin Color: Check for any abnormal skin color changes, such as pallor, cyanosis, or jaundice.
- Skin Temperature: Feel their skin temperature. Is it warm, cool, or clammy?
- Skin Turgor: Assess their skin turgor by gently pinching the skin on the back of their hand. It should return to its normal position without lingering.
- Lesions: Inspect the skin for any rashes, wounds, ulcers, or other lesions. Note their location, size, and appearance.
Cheat Sheet Head To Toe Assessment Form
Putting it All Together
The head-to-toe assessment is a comprehensive approach that allows healthcare professionals to gain an in-depth understanding of a patient’s overall health status. Remember, this is a guide, not a rigid protocol.
The information gathered during this assessment is vital for identifying potential health issues, developing appropriate treatment plans, and ensuring optimal patient care.
By mastering the techniques of head-to-toe assessment, you can become a more effective and confident healthcare provider, making a meaningful difference in the lives of your patients.






