Imagine a world where your basic needs are met – food, water, shelter, safety. You feel secure, but something is missing. A nagging emptiness whispers of a need for something more. This, my friends, is the journey Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs attempts to capture – the human desire for growth and fulfillment. But, is this framework truly the definitive guide to understanding human motivation? A closer look reveals intriguing limitations that challenge the hierarchy’s universality.
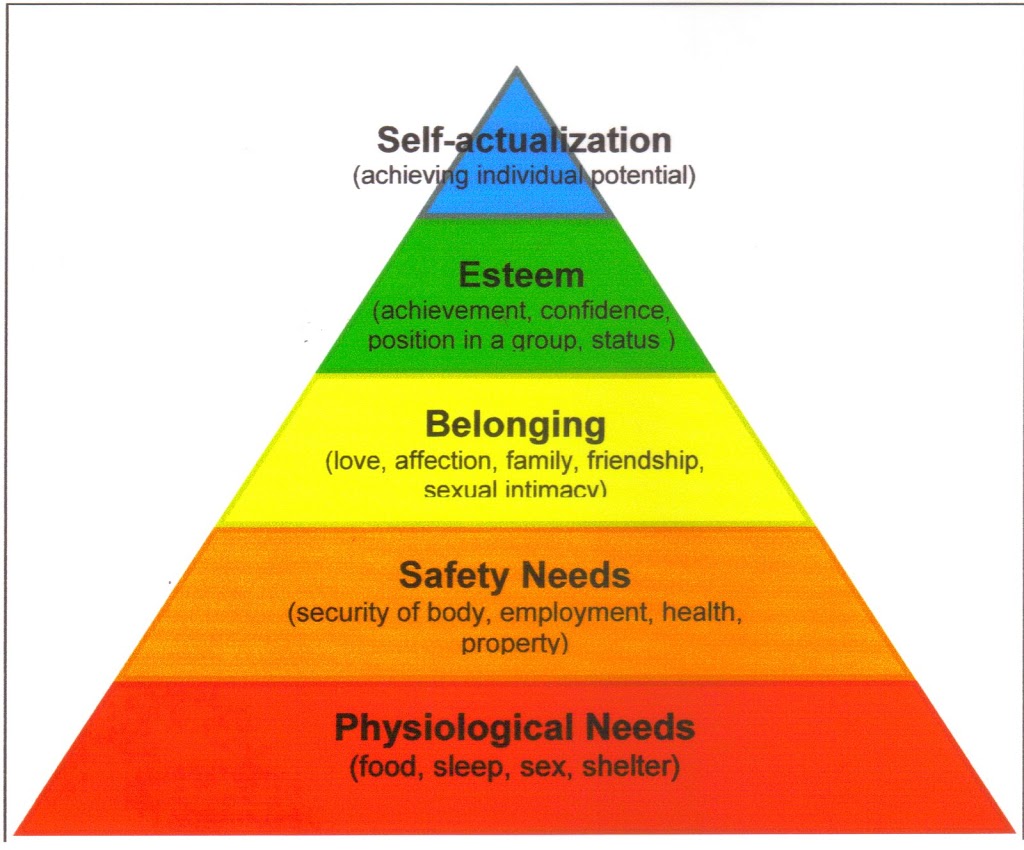
Image: www.hotzxgirl.com
Abraham Maslow’s theory, while insightful and widely popular, paints a simplistic portrait of human motivation. It implies a linear, step-by-step progression, suggesting that once we satisfy lower-level needs, we automatically ascend to the next level. However, the real world, with its complexities and individual nuances, doesn’t always align with this neat framework.
Challenging the Hierarchy’s Rigid Structure
One fundamental flaw in Maslow’s model lies in its rigid structure. The idea that we can neatly categorize needs and move through them sequentially ignores the inherent fluidity and complexity of human desires. For instance, an individual struggling with poverty may still prioritize self-actualization, pursuing their artistic passion despite their lack of basic necessities. This demonstrates that needs aren’t always hierarchical; they can intertwine and exist concurrently.
Cultural Diversity and Individuality
Another limitation stems from the theory’s inability to account for cultural diversity and individuality. Maslow’s model, developed in a specific cultural context, might not accurately reflect the motivations and priorities of other cultures. For example, in collectivist cultures, belonging and social harmony might take precedence over personal achievement, challenging the hierarchical order established by the model.
The Elusive Nature of Self-Actualization
The pinnacle of Maslow’s hierarchy, self-actualization, remains a highly subjective and elusive concept. It represents the pursuit of one’s full potential and can manifest in diverse ways. What constitutes “self-actualization” for one individual might differ significantly from another’s definition. Furthermore, achieving this state is a continuous process, not a final destination, making it difficult to definitively measure or observe.
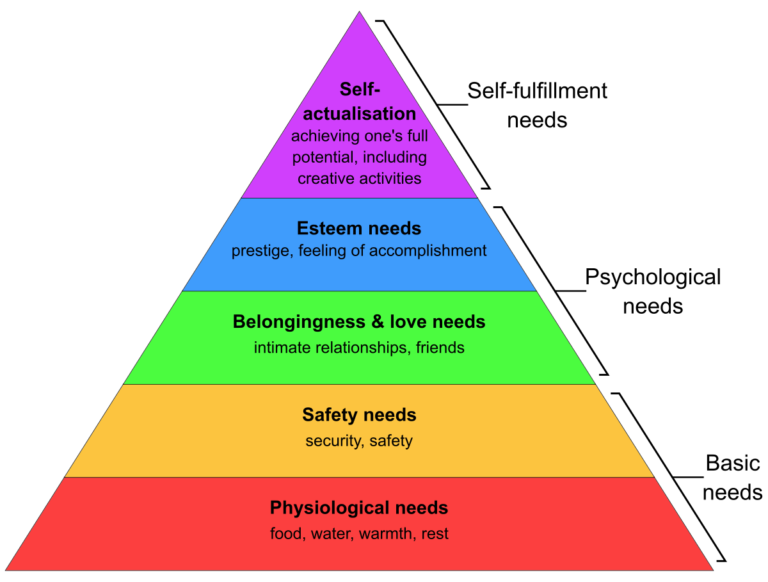
Image: mikaylabinar.com
Oversimplification of Complex Motivations
Maslow’s Hierarchy oversimplifies the intricate web of human motivations, often failing to capture the dynamic interplay between external factors and internal drives. For instance, a person pursuing a career might be driven by a combination of factors: a desire for financial security, a calling for creativity, or a quest for recognition. Reducing such complex motivations to a single, hierarchical category can be misleading.
The Importance of Context and Circumstances
The theory’s static nature ignores the impact of contextual factors and life circumstances. Individual needs and priorities can shift dramatically depending on external influences. A natural disaster, for example, might cause an individual to prioritize safety and survival over self-esteem or social needs. The hierarchy struggles to account for these dynamic shifts in human motivation.
Debunking the Myth of Universal Needs
While Maslow’s model identifies fundamental human needs, it assumes their universality. Research suggests that certain needs, like self-esteem, are not universally valued across cultures or even within individuals. The specific needs that are most salient to individuals will differ depending on their personal history, cultural background, and life experiences.
Lack of Empirical Evidence
Despite its widespread popularity, Maslow’s Hierarchy has faced significant criticism for its lack of empirical support. The model was primarily based on anecdotal evidence and observations of individuals considered self-actualized, making its scientific validity questionable. Rigorous research has shown that human motivation is more complex and less predictable than what the hierarchy suggests.
Beyond the Hierarchy: A More Holistic Approach
Moving beyond the limitations of Maslow’s Hierarchy requires a more holistic understanding of human motivation. Contemporary theories emphasize the interplay between biological, psychological, and social factors, recognizing the fluid nature of human needs and desires. They also acknowledge that individual motivations are shaped by a combination of past experiences, cultural influences, and unique circumstances.
Embracing the Complexity of Human Motivation
The journey of understanding human motivation is an ongoing one. It demands a shift away from rigid frameworks and an embrace of the complexities that define each individual’s path. While Maslow’s Hierarchy provided a valuable foundation for exploring human needs, it’s critical to acknowledge its limitations and embrace a more holistic approach that acknowledges the dynamic interplay of individual and contextual factors.
Limitations Of Maslow’S Hierarchy Of Needs
Final Thoughts
Maslow’s Hierarchy, while offering a valuable perspective, is ultimately a simplified representation of the complexities of human motivation. By acknowledging its limitations and adopting a broader lens, we can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate forces that drive human behavior. Remember, the quest for fulfillment is an individualized journey, and the path to self-actualization is unique to each individual. Let’s embrace the complexities of human motivation and celebrate the diverse ways in which we strive to achieve our potential.






