Imagine a child struggling to keep up in class, constantly fidgeting, and having difficulty finishing their homework. This familiar scene is often the reality for children diagnosed with Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). These conditions present unique challenges for families and require a comprehensive approach to support the child’s learning, behavior, and overall well-being. This is where the nursing care plan for ADHD plays a crucial role in empowering families with the knowledge and strategies essential for navigating these challenges.
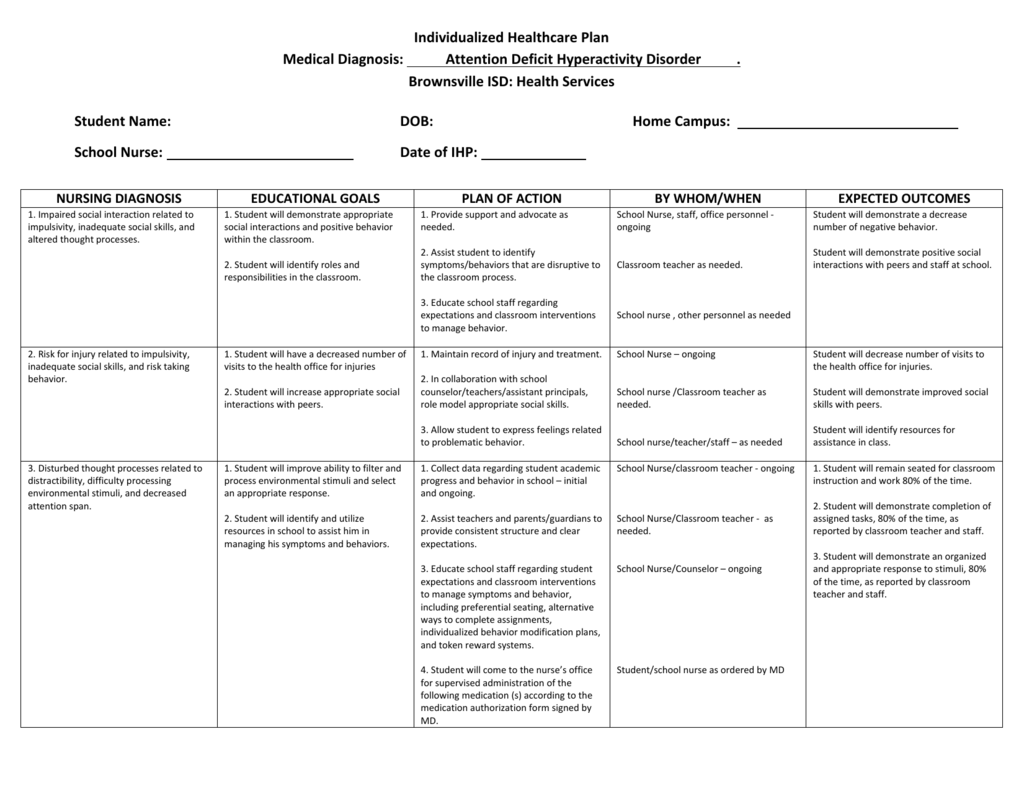
Image: daminmissie.blogspot.com
A nursing care plan for ADHD is a personalized roadmap that outlines specific goals and interventions designed to improve the child’s attention, focus, and overall functioning. It involves a collaborative effort between nurses, doctors, parents, teachers, and the child themselves. Understanding the intricacies of ADHD, the unique needs of each child, and the strategies employed in a nursing care plan can significantly impact a child’s life, paving the way for a brighter and more fulfilling future.
Understanding Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Before delving into the specifics of a nursing care plan, let’s first gain a clear understanding of ADHD. ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with daily life. While the exact cause of ADHD is unknown, research suggests a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Although often perceived as a behavioral issue, ADHD is a real condition that affects the brain’s ability to regulate attention, emotions, and behavior.
It is crucial to differentiate between ADD and ADHD. ADD, or Attention Deficit Disorder, refers to individuals who primarily struggle with inattention, while ADHD involves both inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity. The symptoms of ADHD can vary widely from person to person, making accurate diagnosis and individualized care plans crucial.
A Holistic Approach: Crafting a Comprehensive Nursing Care Plan
A successful nursing care plan for ADHD is built on a holistic approach that addresses the child’s physical, emotional, and social needs. This includes a careful assessment of the child’s symptoms and their impact on daily life. Nurses play a vital role in gathering information through interviews with the child and parents, reviewing medical records, and collaborating with the child’s doctor.
Assessment and Diagnosis
The nursing assessment process begins with gathering detailed information about the child’s symptoms, their onset, and their severity. This involves asking questions about the child’s behavior at home, school, and in social settings. Nurses may use standardized questionnaires and checklists to assess the child’s attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. The assessment also includes evaluating the child’s overall physical health, including any co-existing conditions that might influence their ADHD management.
Once a thorough assessment is conducted, nurses work closely with the child’s doctor to confirm the diagnosis of ADHD. It’s essential to rule out other conditions that could mimic ADHD symptoms before proceeding with treatment. This collaborative approach ensures that the child receives the most accurate and appropriate care.

Image: www.scribd.com
Goal Setting and Intervention
With a confirmed diagnosis in hand, the nursing care plan moves on to establishing individualized goals for the child. These goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), ensuring their practicality and effectiveness. Goals may focus on improving attention, reducing hyperactivity, managing impulsivity, enhancing social skills, and improving academic performance.
The nursing care plan then outlines the interventions and strategies best suited to achieving these goals. These interventions can be broadly categorized into three main areas: behavioral therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications.
Behavioral Therapy: Shaping Behavior and Building Skills
Behavioral therapy is a cornerstone of ADHD management, empowering the child to learn strategies for controlling their behavior and improving their attention. Behavioral therapy focuses on building positive coping mechanisms and reinforcing desirable behaviors. It is implemented through a variety of techniques, including:
- Parent training: Equipping parents with the tools and knowledge to manage their child’s ADHD at home.
- Behavioral management strategies: Using positive reinforcement, rewards, and consistent consequences to encourage desired behaviors.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Teaching children to identify and manage their thoughts and feelings that trigger challenging behavior.
- Social skills training: Helping children develop appropriate social skills, including communication, empathy, and conflict resolution.
Medication: Balancing Brain Chemistry
Medication is a crucial part of ADHD management for many children, particularly when behavioral therapy alone is insufficient. However, it’s essential to emphasize that medication is a tool to be used in conjunction with other interventions, not a standalone solution. Medication aims to balance brain chemicals associated with attention, focus, and impulsivity, helping improve symptoms like inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
Nurses play a crucial role in educating families about the different types of medication used for ADHD, their potential benefits and side effects, and the importance of regular monitoring. It’s crucial to manage medications carefully, adhering to prescribed dosages and schedules. Nurses also work with families to address any concerns or questions they may have about medication safety and appropriateness.
Lifestyle Modifications: Creating a Conducive Environment
Lifestyle modifications encompass changes in routine, diet, and environment that can positively impact a child’s attention and behavior. These modifications can be implemented in conjunction with behavior therapy and medication, creating a comprehensive approach to ADHD management.
- Structured routine: Establishing a consistent daily schedule can help regulate a child’s energy levels and improve focus. This includes regular sleep schedules, mealtimes, and activity breaks.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support healthy brain function and reduce impulsivity.
- Regular physical activity: Exercise has been shown to improve attention, focus, and mood in children with ADHD. Encourage regular exercise, such as sports, dancing, or outdoor play.
- Quiet time and relaxation: Providing opportunities for calming activities, such as reading, yoga, or meditation, can help reduce stress and improve focus.
Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments
The nursing care plan is not a static document but rather a dynamic roadmap that evolves as a child’s needs change. Regular monitoring is crucial to assess the effectiveness of interventions and make necessary adjustments. Nurses play a critical role in this monitoring process, collaborating with parents, teachers, and the child’s doctor to track progress.
This ongoing assessment involves collecting information about the child’s behavior, academic performance, and overall well-being. It may involve periodic reviews of the child’s symptoms, medication effectiveness, and response to behavioral therapy. Based on this assessment, the nursing care plan may be adjusted to ensure it remains well-suited to the child’s evolving needs.
Nurturing Self-Esteem and Building Confidence
Living with ADHD can pose unique challenges for a child’s self-esteem and social interactions. A supportive and encouraging environment is crucial for helping children manage their condition and develop a positive sense of self. Nurses play a crucial role in empowering children with a sense of agency and self-belief by promoting a positive self-image and helping them understand their strengths.
This involves engaging the child in open and honest conversations about their ADHD, dispelling any negative stereotypes, and celebrating their achievements and strengths. It also involves working with parents and teachers to create a supportive and understanding environment that values the child’s unique abilities and perspectives. By fostering a positive self-image, nurses can help children build confidence and resilience, enabling them to overcome challenges and thrive.
Creating a Supportive Network for Success
Effective ADHD management requires the involvement of a robust support network that extends beyond the medical team. This network includes parents, teachers, school staff, and other professionals who can play a vital role in supporting the child’s well-being.
Nurses can facilitate this collaborative approach by providing clear communication channels between different stakeholders, ensuring everyone has access to the information they need to support the child’s success. This includes sharing the nursing care plan, providing educational resources, and organizing meetings and workshops to foster collaboration and understanding.
Empowering Families and Building Resilience
A successful nursing care plan for ADHD is not just about managing symptoms; it’s about empowering families and equipping them with the tools and knowledge they need to navigate this complex journey. Nurses play a crucial role in fostering a sense of optimism and hope, helping families understand that ADHD is not a life sentence but rather a condition that can be effectively managed with the right support and intervention.
By providing families with accurate information, educational resources, and a sense of partnership, nurses can help them develop a positive outlook and a sense of agency in their child’s care. This empowered approach empowers families to take an active role in their child’s treatment, encouraging them to embrace their strengths and navigate challenges with resilience and confidence.
Nursing Care Plan For Attention Deficit Disorder
Conclusion: A Journey Towards Success
Navigating the challenges of ADHD can be a journey that requires patience, understanding, and a collaborative approach. Nursing care plans play a pivotal role in guiding families towards success by providing personalized strategies, fostering a supportive environment, and empowering children and families to embrace their strengths. Through assessment, goal setting, intervention, ongoing monitoring, and a focus on building resilience, nursing care plans can significantly improve the lives of children with ADHD, paving the way for a bright and fulfilling future.
If you are a parent or caregiver facing the challenges of ADHD, remember that you are not alone. Connect with medical professionals, educators, and other families facing similar challenges. Embrace the tools and resources available, nurture your child’s strengths, and celebrate every milestone on their journey. With the right support and guidance, children with ADHD can thrive, learn, and lead fulfilling lives.






